Fine-Tuning VLM: Enhancing Geo-Spatial Embeddings
As the world generates an ever-expanding volume of visual content, the need for efficient data curation becomes increasingly important. Whether it’s satellite imagery, aerial photographs, or remote sensing data, organizing and annotating these visuals is essential for scientific research, urban planning, disaster response, and more.
In this blog post, we explore how fine-tuning the Contrastive Language-Image Pre-Training or CLIP model with the RSICD dataset—a collection of remote sensing images and captions—revolutionizes how we curate geospatial data. Unlike traditional image processing methods, CLIP offers advanced capabilities like semantic search and multilingual annotations, improving the processing and analysis of geospatial information.
Fine-Tuning Vision-Language Models (VLMs)
Fine-tuning Vision-Language Models (VLM) to enhance embeddings is a cutting-edge approach to data curation. VLMs are advanced models that combine visual and textual understanding, making them incredibly powerful tools for processing and analyzing multimedia data.
By fine-tuning these models specifically for geospatial tasks, we aim to improve location-based data processing and analysis accuracy and efficiency.
Geo-spatial Embeddings
Geo-spatial embeddings refer to representations of geographical locations in a continuous vector space, where each location is encoded as a vector with semantic meaning. These embeddings are crucial for various applications such as geographical information systems (GIS), location-based recommendation systems, urban planning, environmental monitoring, and disaster response.
However, generating accurate geospatial embeddings from heterogeneous data sources poses significant challenges due to the complexity and diversity of spatial information.
At Encord, we address these challenges by fine-tuning VLMs like CLIP to produce more accurate and semantically rich geospatial embeddings. This can help streamline your data curation process with new possibilities for using geospatial data.
Importance of Fine-Tuning VLM in Data Curation
The importance of fine-tuning VLMs in data curation can be understood through several key aspects:
Semantic Understanding
VLMs are capable of understanding and interpreting both visual and textual information simultaneously. By fine-tuning these models on specific datasets relevant to a particular domain, such as medical imaging or satellite imagery, they can learn to associate visual features with corresponding textual descriptions.
This semantic understanding greatly enriches the curated data by providing context and meaning to the information being processed. So, the annotators can quickly identify and tag images based on textual descriptions, improving dataset organization and curation.
Adaptability to Domain-Specific Requirements
Different domains have unique data characteristics and requirements. Fine-tuning VLMs allows for customization and adaptation to these domain-specific needs. For example, here we are fine-tuning the VLM model to improve geospatial embeddings.
Improved Data Accuracy
Fine-tuning VLMs enables them to better capture the complexities of curated data. This results in improved relevance and accuracy of the curated datasets as the models learn to extract and highlight the most relevant features and information. Consequently, curated datasets become more valuable for downstream tasks such as machine learning, analytics, and decision-making processes.
Fine-Tuning CLIP with RSICD
CLIP
Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training or CLIP, developed by OpenAI, is a powerful multimodal model that bridges the gap between natural language and visual content. It learns to associate images and their corresponding captions in a self-supervised manner, enabling it to perform tasks like image search, zero-shot classification, and more.
RSICD Dataset
The Remote Sensing Image Caption Dataset or RSICD serves as our training ground. Comprising approximately 10,000 satellite images, this dataset features image labels and descriptive captions. These captions provide valuable context, making RSICD an ideal candidate for fine-tuning CLIP.
Why Fine-Tune CLIP with RSICD?
Geo-Spatial Specificity
Satellite images differ significantly from everyday photos. They are satellite-captured images that differ from typical ground-level images in scale, perspective, and resolution. By fine-tuning CLIP with RSICD, we tailor the model to understand the complexities of geospatial data. This specificity enhances its ability to handle satellite imagery effectively.
Strengthen Search Ability
By incorporating captions during fine-tuning, we ensure that the model cohesively embeds both image and text information. Consequently, CLIP becomes adept at natural language search and image retrieval.

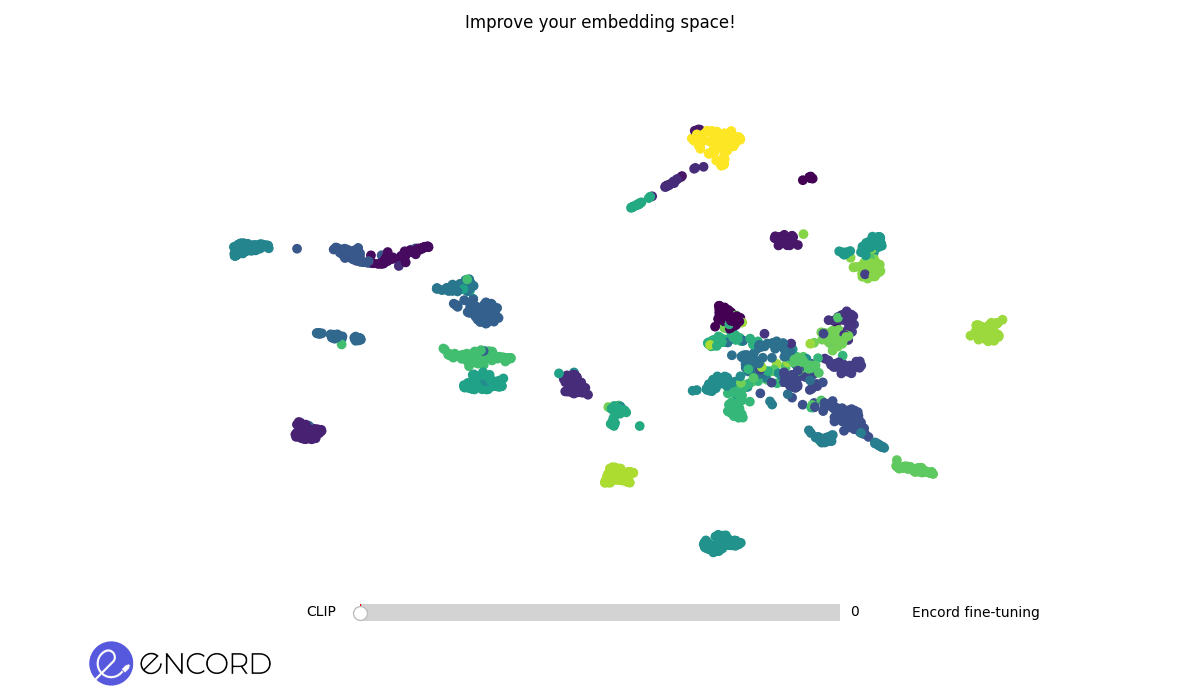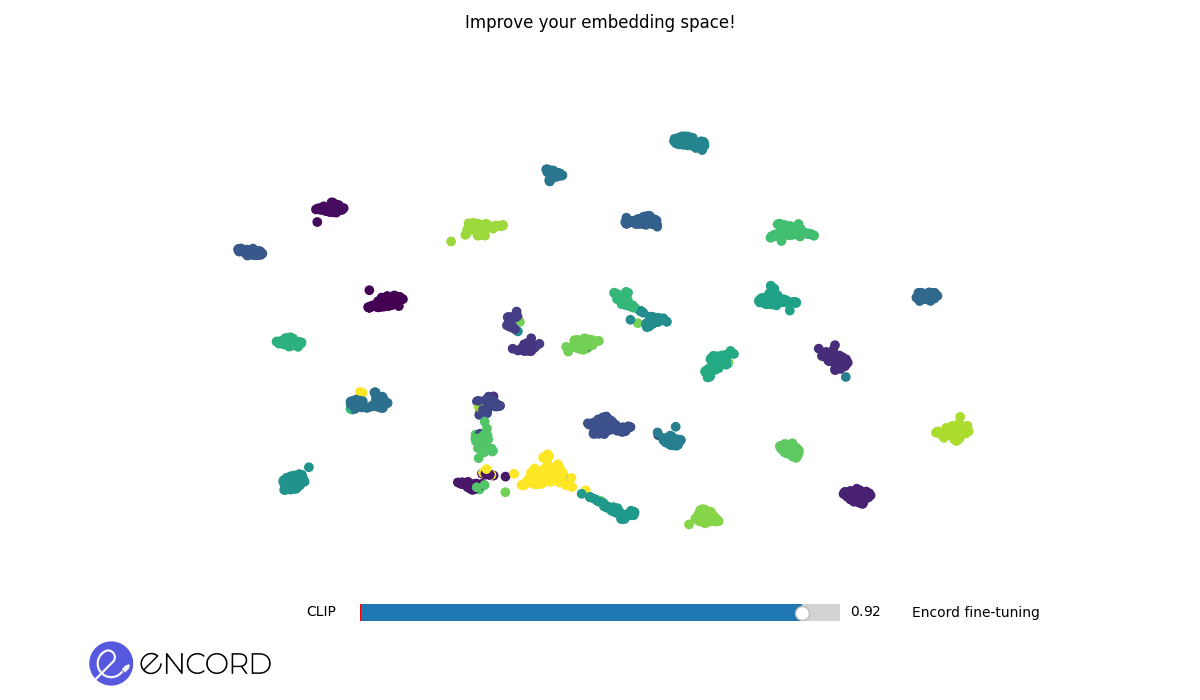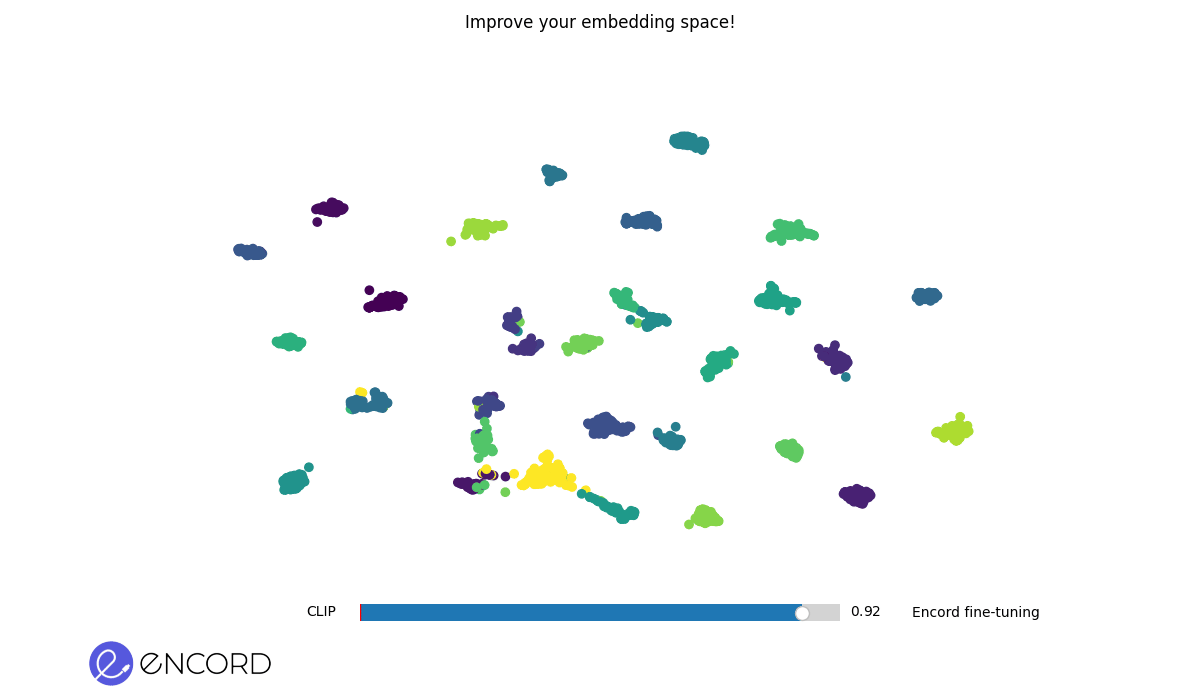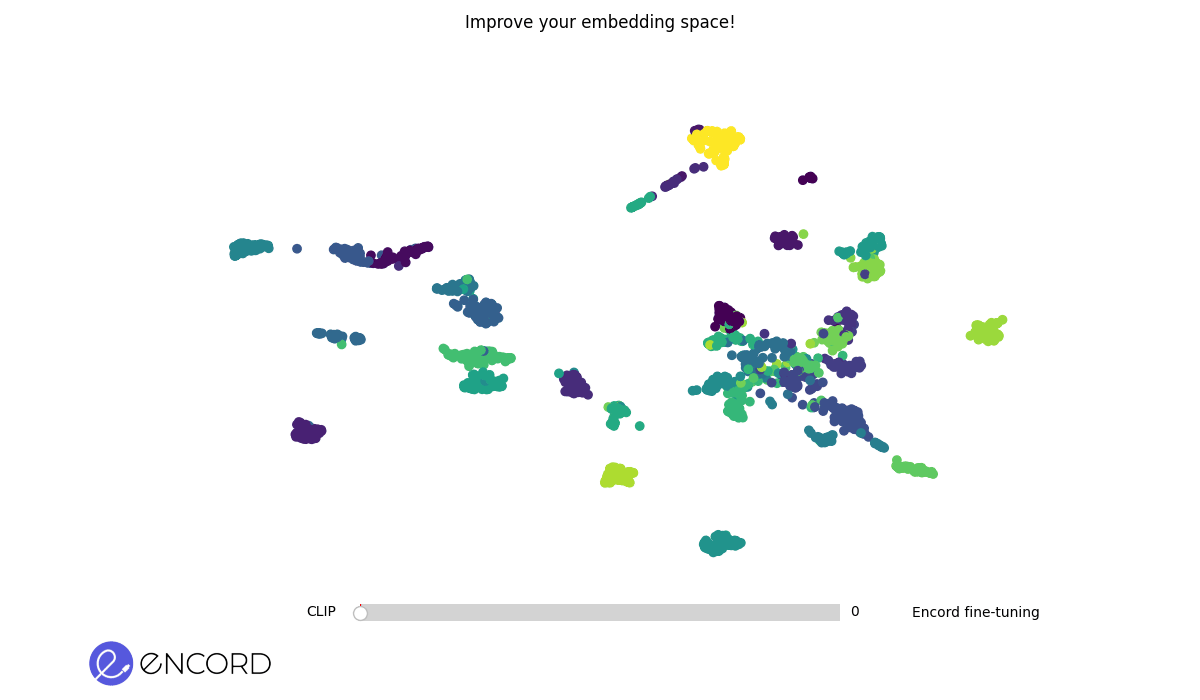
Embedding Space Before Fine-Tuning. The scattered arrangement of clusters represents data points in the initial embedding space.
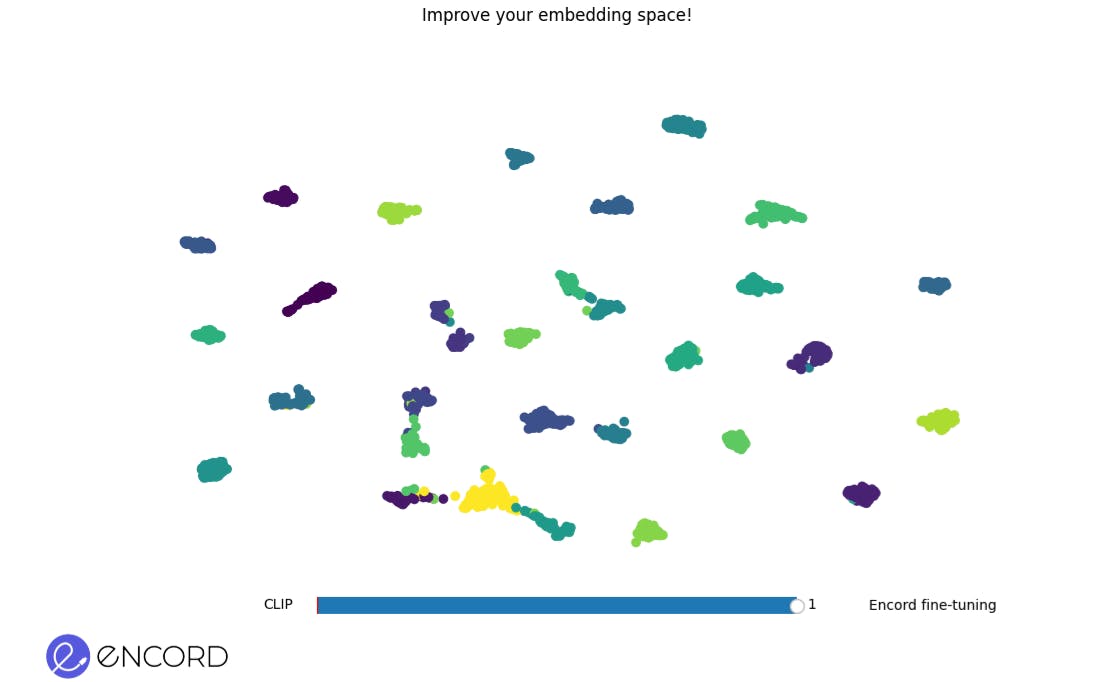
Embedding Space After Fine-Tuning. A more refined and cohesive grouping of data points indicates an improved embedding space post-fine-tuning.
Zero-Shot Performance Evaluation
We evaluate the model’s zero-shot performance using ground truth labels. This involves assessing whether the textual embeddings align with the image embeddings. Such alignment validates the consistency of CLIP’s image-text capabilities.
Significance of Fine-Tuning CLIP with RSICD
Geo-Spatial Annotation Precision
- Contextual Understanding: RSICD provides satellite images alongside descriptive captions. By fine-tuning CLIP, we enhance its ability to understand the nuances of geospatial features—mountains, rivers, forests, urban areas, and more.
- Accurate Labeling: Curators can annotate images with greater precision. Whether identifying specific land cover types or pinpointing landmarks, CLIP ensures context-aware annotations.
Efficient Data Exploration
- Semantic Search: Curators and researchers can query the dataset using natural language. CLIP retrieves relevant images based on textual descriptions. For instance, searching for “coastal erosion” yields coastal satellite imagery.
- Time Savings: Manual exploration of thousands of images becomes streamlined. CLIP acts as a smart filter, presenting relevant visuals promptly.
Consistent Labeling and Quality Control
- Alignment of Embeddings: During fine-tuning, CLIP learns to align image embeddings with textual embeddings. Curators can cross-check whether the textual descriptions match the visual content.
- Uniform Annotations: Consistent labeling improves model training and downstream tasks. Whether detecting deforestation or urban sprawl, CLIP ensures uniformity.
In summary, fine-tuning CLIP with RSICD empowers data curators by providing efficient search, consistent labeling, multilingual support, and domain-specific expertise. As we embrace this powerful tool, we pave the way for smarter, more accessible datasets.
Frequently asked questions
Encord is built to handle scalability, allowing teams to start with small proof-of-concept datasets and gradually scale up to larger, countrywide data. This flexibility is essential for projects that need to adapt to customer requirements and expand their analytical capabilities over time.
Yes, Encord is designed to support model fine-tuning by allowing users to annotate new varieties of crops, such as raspberries. With a focus on collecting and labeling a diverse range of images, Encord provides the tools necessary to prepare data sets for effective model training.
Encord provides tools that streamline the annotation process for various data types, including 2D images and 3D point clouds. Our platform enables users to manage and adjust annotations efficiently, reducing the manual effort typically required in complex tasks like bin picking.
Encord streamlines the data curation process by providing interactive filtering options, such as embeddings and quality metrics. This not only enhances the speed of data processing but also improves the overall quality of the datasets used for machine learning projects.
Encord provides capabilities to leverage multiple models in conjunction with human input to enhance the accuracy and efficiency of geospatial analysis. This allows for more effective data handling in complex projects, such as those involving construction technology.
Yes, Encord is designed to facilitate bounding box annotations among other annotation types. The platform allows customization of how bounding boxes are displayed, providing flexibility to users based on their specific project requirements.
Yes, Encord supports complex overlapping annotations, including those needed for grape data, using polygon annotation. This enables users to accurately annotate clusters and berries without the limitations found in bitmap annotations.
Yes, Encord's tools are versatile, offering general habitat mapping applicable to any location, as well as specialized assessments for unique habitat types to meet specific ecological research needs.
Encord allows users to adjust polygon vertices and provides additional editing tools such as brush features, which enhance flexibility in creating and modifying annotations within the platform.
