Contents
Reinforcement Learning (RL) Basics
The Concept of Reinforcement Learning in AI
Overview of RLHF
Limitations and Ethical Concerns Associated with RLHF
Broader Ethical Implications of RLHF
Mechanics of RLAIF
RLAIF Process
The RLAIF Process and Constitutions: Creating the Harmlessness Dataset
What is RLAIF: Key Takeaways
Encord Blog
What is RLAIF - Reinforcement Learning from AI Feedback?
Language models like GPT-4 have significantly progressed in writing code and drafting documents. However, their development faces challenges, particularly in safety and ethical considerations. One prominent technique in aligning these Large Language Models (LLMs) with human values is Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF). In RLHF, LLMs are trained to generate helpful outputs and align with human preferences. Yet, this technique encounters challenges due to its reliance on human-generated feedback, which has scalability and resource allocation limitations.
Addressing these challenges, Reinforcement Learning from AI Feedback (RLAIF) emerges as a novel approach. RLAIF employs another AI model for feedback, guided by a set of principles outlined in a constitution. This constitution is crucial as a guideline to ensure the AI’s feedback aligns with ethical and safety standards. RLAIF retains the beneficial attributes of RLHF, such as generating helpful outputs, but also makes strides in enhancing safety, reducing subjectivity, and improving scalability. By automating the reference annotation process with AI, RLAIF solves the problem of collecting extensive human feedback, making the learning process more efficient.
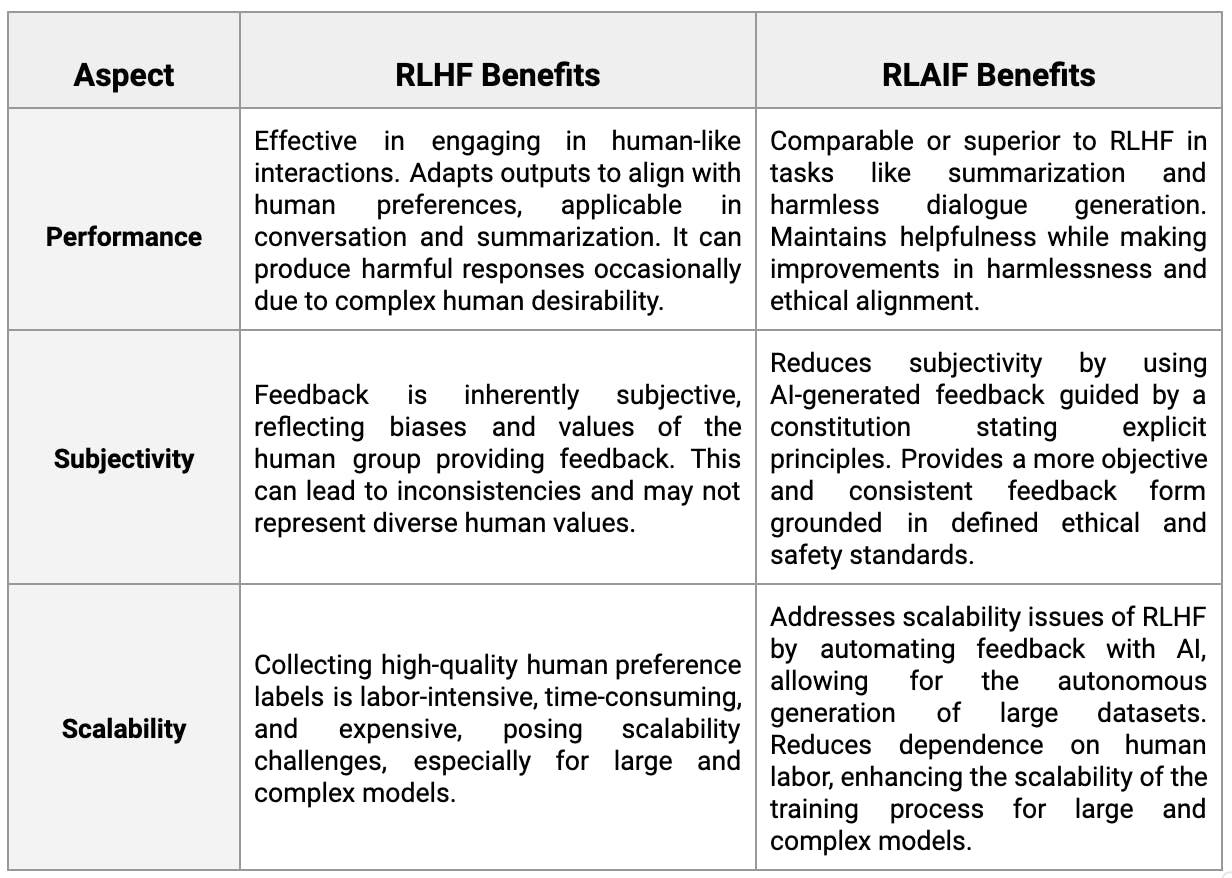
One of the key aspects contributing to the effectiveness of RLAIF is its advanced prompting techniques, which improve AI-generated feedback by providing examples and guiding thoughts for consistency. This method enables AI models to match human preferences with minimal human involvement. Research indicates that AI models trained with RLAIF perform comparably to those trained with RLHF, particularly in tasks like text summarization. RLAIF stands out as a scalable and efficient alternative to traditional reinforcement learning methods, achieving similar performance levels with reduced need for human annotations.
This article will provide an in-depth look at the mechanisms and implications of RLAIF, illustrating how it addresses the limitations of RLHF and opens new avenues for developing safe and ethical AI systems.
Reinforcement Learning (RL) Basics
Reinforcement Learning (RL) is artificial intelligence that helps with decision-making and motor control. It works by trying different actions in an environment to get the best overall result. People learn from experience by understanding that actions have consequences. These consequences can impact future behavior.
The Concept of Reinforcement Learning in AI
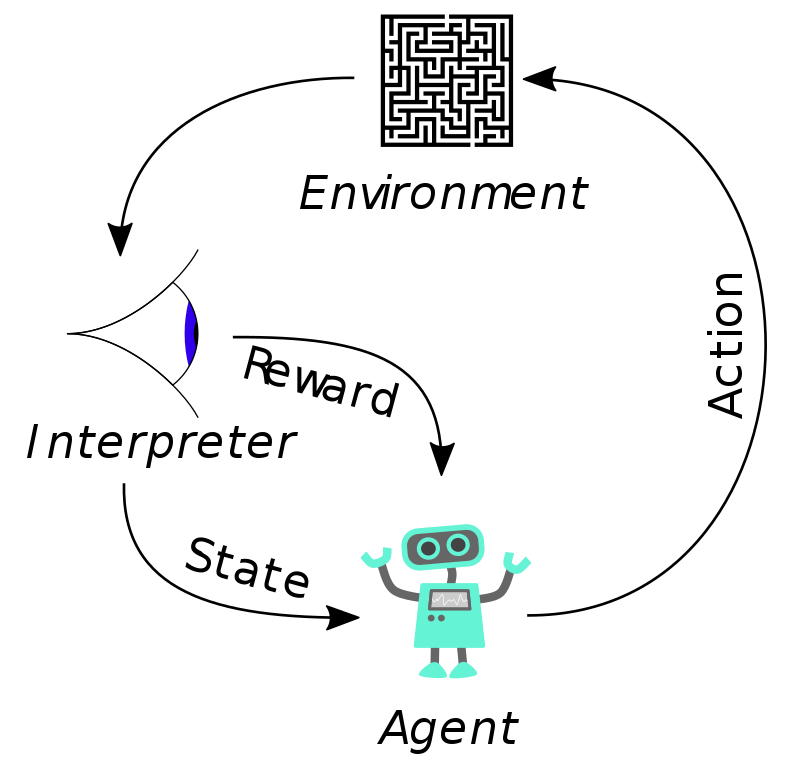
At the core of RL are two main entities: the agent and the environment.
The agent represents the decision-maker. The environment embodies the world where the agent operates. During each interaction step, the agent gets a state observation from the environment and chooses an action.
The environment then responds to this action, leading to a new state and providing a reward signal to the agents. This reward signal is a numerical value indicating the desirability of the state resulting from the agent's action. The agent's objective is to maximize the total rewards, known as the return, over time.
Use of Reward Signals
The reward signal in RL is pivotal, guiding the agent's learning process. It varies based on the current state of the world, the action taken, and the next state. This signal can depend on the current state or the state-action pair. The agent aims to gather as many rewards as possible during a trajectory. You can have two types of trajectories: finite horizon and infinite horizon. The finite-horizon trajectory adds rewards for a set number of steps—the infinite-horizon trajectory discounts future rewards based on time.
The RL optimization problem involves choosing a policy that maximizes expected return. A policy is a strategy the agent employs to decide actions based on the current state. The challenge is to find the best policy, called \(\pi^*\), that gives the highest expected return in all state paths. To do this, you need to figure out how likely different paths are and what rewards each one has. You have to consider all the possible paths the agent could choose.
Overview of RLHF
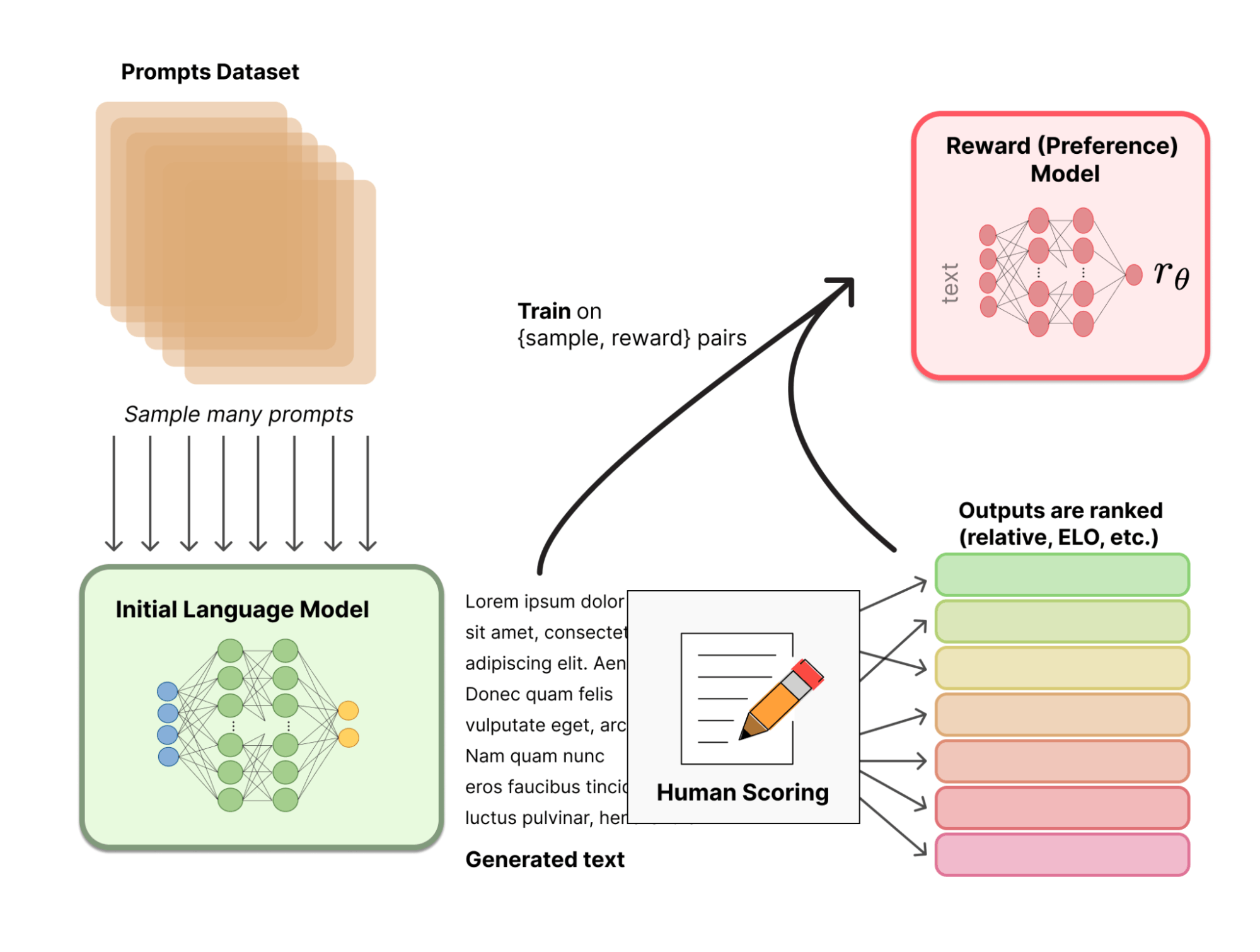
When human feedback is added to reinforcement learning, AI applications align more with human goals. RLHF improves AI models' efficiency by enhancing their understanding and generation of language. It also helps with tasks like text classification and translation.
An agent in reinforcement learning learns to make decisions by interacting with its environment. It receives feedback to adjust its decision-making. RLHF improves this process by involving humans through feedback to fine-tune the reward function that guides the learning process of the AI. It focuses on aspects that automated reward systems can't measure. Human evaluators help train the reward model by giving feedback. This balances machine learning with human understanding.
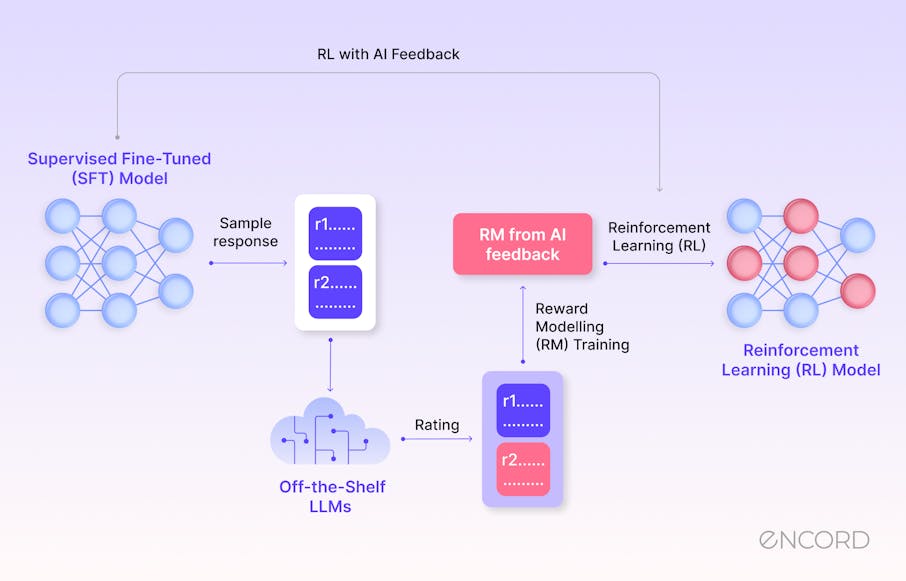
RLAIF marks a significant evolution in training AI assistants, primarily addressing the challenges of Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF). RLAIF differs from RLHF in its use of AI-generated feedback for training, guided by a constitution that sets forth ethical and safety principles.
This approach ensures that the AI's behavior aligns with these predefined standards, thus enhancing ethical alignment and reducing the subjectivity inherent in human feedback. By automating the feedback process, RLAIF also overcomes scalability issues associated with human-based feedback, making it a more efficient method for training AI on a large scale. The constitution in RLAIF is crucial as it clearly outlines the expected behavioral principles for the AI, ensuring that the training is rooted in ethical considerations and safety standards.
In the RLAIF training process, an AI model, known as the Feedback Model, evaluates responses generated by an AI assistant (Response Model) to various prompts based on constitutional principles. The process begins with generating and revising responses to elicit safe and ethical outputs, then fine-tuning the AI assistant with these revised responses.
Limitations and Ethical Concerns Associated with RLHF
Despite its advantages, RLHF faces several challenges and ethical considerations:
Human Involvement Challenges
One of the critical limitations of RLHF is the bias inherent in human-provided feedback. Since RLHF relies heavily on human judgment for its learning signals, the AI model may adopt the evaluators' biases. This can affect the learning outcome of the AI model and potentially lead to biased outputs.
Process Bottleneck
Human labor for data labeling in RLHF can be slow and costly. It often becomes a bottleneck in the process, limiting the scalability and efficiency of the model training.
Maintaining Language Consistency and Model Integrity
LLM should stay within the original model while improving its responses. This balance is crucial to preserving the language model's integrity and reliability.
Complexity of a Universal Reward System
Creating a reward system that satisfies everyone is challenging because of individuals' and groups' varied preferences and values. This complexity makes it challenging to ensure the AI model aligns perfectly with all user expectations, leading to potential misalignments with certain groups or cultural contexts.
Broader Ethical Implications of RLHF
Misinformation and Social Impact
RLHF, while effectively aligning AI systems with human values, can be misused for misinformation or perpetuating societal prejudice. The power of RLHF in content generation, particularly in the context of disinformation and automated trolling, can undermine public trust in media and governance. This misuse highlights the need for careful governance and oversight of RLHF applications.
Alignment with Human Values
AI research aims to create systems aligned with human values and intentions. RLHF is a step forward but faces challenges in ensuring accurate inner alignment without ulterior motives. The design of RLHF models must consider fundamentally conflicting feedback and preferences and reconcile them in a way that respects diverse moral beliefs and cultural contexts.
Transparency and Accountability
Increasing transparency in developing and deploying RLHF-trained models is crucial for safety and accountability. Disclosing details behind RLHF training runs and efforts to mitigate risks can improve industry norms, support societal oversight, and enhance the AI community’s understanding of RLHF.
Fundamental Limitations
It's essential to recognize that some challenges with RLHF are fundamental and cannot be solved entirely. These limitations necessitate using defense-in-depth safety measures and sharing research findings to understand better and address these challenges. Researchers must also communicate their work to the public and media outlets transparently to avoid misinformation and increase digital literacy.
Governance and Oversight
Addressing governance of infrastructure supporting RLHF applications and developing early warning systems for disinformation campaigns are critical. This involves cooperation between governments and industry parties and developing formalized guidelines for guarding against misuse and recommending mitigations.
While RLHF offers significant benefits in AI alignment and content generation, it also presents substantial challenges and ethical concerns that must be addressed through careful research, transparent governance, and ethical considerations in its application.
Mechanics of RLAIF
Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) aligns large language models (LLMs) with human preferences. In RLHF, the process involves taking a pre-trained LLM and exposing it to rewards or punishments based on human judgment of its outputs. This method helps the model act better by being more friendly and helpful. However, a significant limitation of RLHF is the need for extensive human feedback. Collecting suitable preference labels from people can be expensive, take a lot of time, and be challenging to do on a large scale.
Reinforcement Learning from AI Feedback (RLAIF) is a pivotal shift to tackle these challenges. This approach combines RL algorithms with feedback from other AI models (Preference Model (PM)) for hybrid learning. The RLAIF system uses AI-generated feedback to help the learning agent make better decisions. Changing from RLHF to RLAIF solves the problem of limited human feedback in RLHF. This makes the learning process more efficient and scalable.
Fundamental Benefits of RLAIF Over RLHF
RLAIF Process
Here's a detailed breakdown of RLAIF's process and how it generates and uses AI feedback:
Step 1: Generate Revisions
- Initial Response Generation: We use a helpful RLHF model to generate responses. However, it can sometimes produce harmful ones.
- Critique and Revision: The response is reviewed for harmful aspects, such as unethical or illegal content, based on certain principles. The model then revises the answer to eliminate these harmful elements.
- Iterative Process: Repeat critiquing and revising using random constitutional principles multiple times. This refines the response, making it harmless and non-evasive.
Step 2: Fine-Tune with Revisions
- Creation of SL-CAI Model: Create a pre-trained model by finetuning the datasets of prompts and the revised responses from Step 1. This model is called the SL-CAI (Supervised Learning for Constitutional AI) model. This model becomes the Response Model in the next step and the basis for the final model after the RL phase.
- Purpose of Fine-tuning: Fine-tuning prepares the SL-CAI model to generate better responses. It also helps reduce the need for later RL training.
Step 3: Generate Harmlessness Dataset
- Using the SL-CAI Model: This model generates two responses to harmful prompts.
- Feedback Model Evaluation: A Feedback Model evaluates the responses using constitutional principles, presented as multiple-choice questions. This creates a dataset of preferences, with normalized probabilities as scores for each response.
Step 4: Train Preference Model
- Preference Model Pre-training (PMP): The Preference Model (PM) is pre-trained using the harmlessness dataset before training. The "Harmlessness Dataset" in the context of AI and machine learning refers to data collection used to train AI systems to avoid harmful, unethical, or inappropriate responses, ensuring their interactions are safe and respectful. This training helps the PM improve using information from websites like Stack Exchange. It is particularly useful when there is little data available.
- Training the PM: The PM uses comparison data from the harmlessness dataset. This allows it to assign preference scores to input pairs (prompt/response).
Step 5: Reinforcement Learning
- Application of Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO): We use Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) to train the SL-CAI model. PPO helps optimize the policy mapping from prompt text to response text.
- Using PM as a Reward Signal: The PM's output from the previous stage is used as the reward signal for training the SL-CAI model in this RL stage.
Additional Considerations
- Contrast with RLHF: Unlike RLHF, which relies on human-generated preference data, RLAIF automates this process using AI feedback based on constitutional principles.
- Ethical and Practical Benefits: RLAIF addresses the ethical concerns and inefficiencies of RLHF by using AI feedback, leading to more scalable and potentially more ethically sound models. From an ethical standpoint, RLAIF offers a more controlled and consistent environment for training AI models. Traditional reinforcement learning (RL) learns from trial and error in a simulated environment, which is advantageous when ethical rules are not consistently agreed upon or are situation-dependent. RL's ability to adapt and learn from a dynamic environment makes it a suitable candidate for teaching ethics to AI systems.
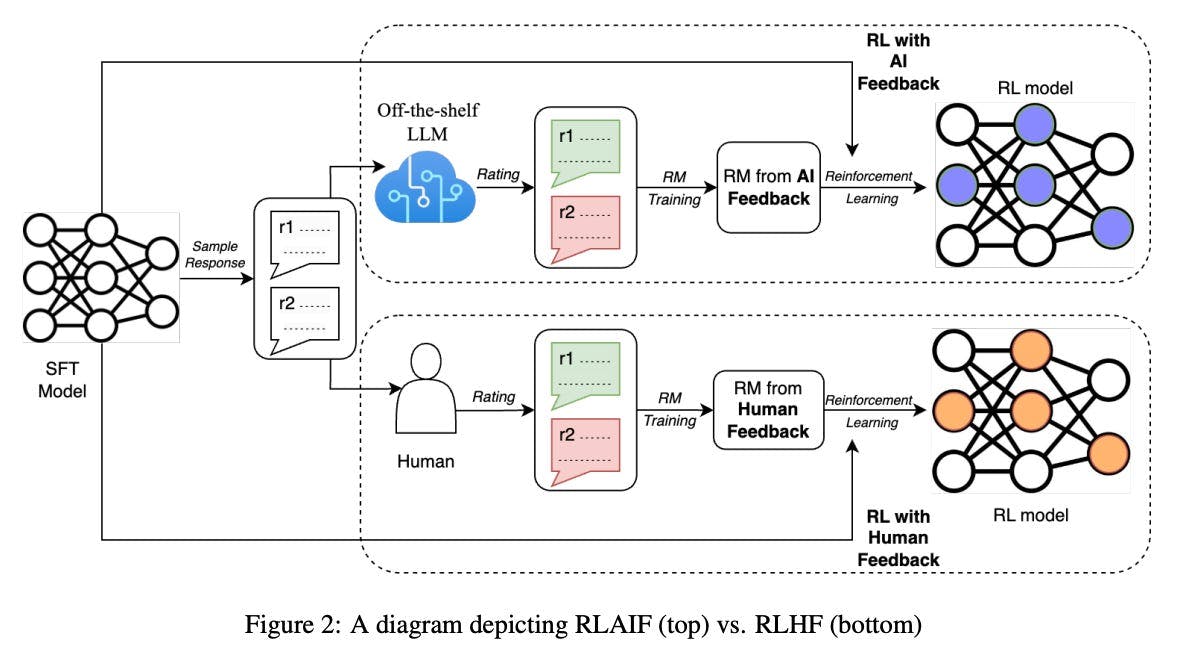
RLAIF is a complex method that uses AI feedback, model training, and revision processes. The aim is to create AI responses that are useful and safe, with less reliance on human feedback and improved efficiency and ethics in AI training.
The RLAIF Process and Constitutions: Creating the Harmlessness Dataset
To make AI harmless and honest in Constitutional AI (CAI), we must create the “Harmlessness Dataset.” This involves training AI systems to be harmless and honest. We do this because AI capabilities are getting closer to or surpassing human-level performance. The process described in a research paper on CAI has two main stages. The first stage is supervised learning (SL), and the second stage is reinforcement learning (RL), also known as RL from AI Feedback (RLAIF).
Supervised Learning (SL) Stage
In the SL stage, the AI initially responds to prompts designed to elicit harmful responses using a "helpful-only" assistant. These initial responses are often harmful or toxic. The model is then prompted to critique its response based on principles or a "constitution." After critiquing, it revises its initial response in light of the critique. This process of critique and revision is repeated, drawing on various principles from the Constitution each time. This process helps improve the model's responses to match the desired behavior. It allows for adjustments. The revised responses improve a pre-trained language model through supervised learning. During this stage, we shape the model's early behavior. This makes it less likely to explore and shortens the training time in the next RL phase.
Reinforcement Learning (RLAIF) Stage
In the RL stage, the process mimics RLHF. It replaces human preferences with AI-generated feedback. This feedback is based on constitutional principles and focuses on harmlessness. The AI compares pairs of responses to each prompt. It decides which response aligns more with a constitutional principle. The evaluation creates an AI preference dataset for harmlessness. It's mixed with human feedback data on helpfulness. A preference model (PM) is then trained on this combined data.
In the last step, we will fine-tune the AI assistant using the SL training method. This will result in a policy trained with RLAIF. This method improves the AI's ability and trustworthiness. It also emphasizes transparent decision-making and explains the AI's reasoning.
We want to develop this CAI technique for a few reasons:
- First, we want to find better ways to supervise AI.
- Second, we want to improve existing models by making their responses less evasive.
- Third, we want to increase transparency in AI decision-making.
- Finally, we want to rely less on human feedback to train harmless AI systems.
This new approach improves AI training, allowing us to create helpful and honest AI systems. It takes work to achieve this balance with traditional methods. The RLAIF process, coupled with the development of the Harmlessness Dataset, facilitates the training of AI models to strike a balance between helpfulness and harmlessness. By using constitutional principles, we can make AI systems more autonomous and responsible.
The Constitution in RLAIF
The RLAIF's Constitution is a guide that outlines principles for the AI's decision-making process. The RLAIF method relies on this constitution to guide AI models to act ethically.
The constitution of RLAIF plays a crucial role in guiding the AI's feedback and responses. The AI must follow guidelines when responding to prevent harmful or unethical outputs. The constitution reduces the risks of AI responses by ensuring they follow ethical standards. In a field where AI is advancing quickly, it is crucial to consider potential harm.
The constitution helps make AI models safer and improves RLAIF models compared to RLHF. RLAIF models are as helpful as RLHF models but are also much safer. The constitution-driven RLAIF method is less subjective. It relies on something other than a small pool of humans and their preferences, like RLHF. Lastly, RLAIF is a more scalable supervision technique than RLHF, guided by the constitution.
The Constitutional AI used in RLAIF has been distilled into nine core principles, each addressing a different aspect of AI behavior:
- Models should not promote harmful content. To ensure the content is right, don't include anything that is unfair, mean, harmful, against the law, insensitive, rude, unjust to gender, or unfair to a group of people.
- Positive direction in conversations: Models should aim to steer conversations towards positive outcomes.
- To address harmful assumptions, the model should politely point them out if a human makes them.
- The model should address assumptions humans make that cause problems.
- Age-appropriate content: The model should avoid providing unsuitable content for all ages.
- Legality and safety: Models should not provide legally questionable or dangerous advice.
- Please provide non-controversial responses that align with moral and ethical standards.
- The model should respond like a caring friend or therapist, showing empathy and sensitivity.
- The model should not assist with criminal activities like violence, theft, hacking, or robbery.
The RLAIF constitution guides how AI models behave to ensure they follow ethical and social rules. It also keeps them helpful and scalable.
What is RLAIF: Key Takeaways
Reinforcement Learning from AI Feedback (RLAIF) is a big step forward compared to Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF). It's especially useful for large language models like GPT-4. RLAIF is better because it can handle more data at scale and is more efficient. It uses AI-generated feedback instead of human feedback. This shift to AI-generated feedback enhances the efficiency and speed of training AI systems. Additionally, RLAIF optimizes the AI's ability to align with desired outcomes, although it may not directly improve understanding human preferences.
RLAIF uses a Preference Model (PM) that follows constitutional principles. This ensures that AI responses are ethical, safe, and high-quality. The constitution sets rules for AI decision-making. It makes sure AI follows ethical and social standards. This is important as AI keeps evolving. RLAIF is moving towards an automated, moral feedback system focusing on responsible AI governance and ethical guidelines.
Explore our products
- RLAIF is an advanced AI training method. It is essential for transformer-based models like GPT-4. It utilizes feedback from AI models rather than relying on human feedback. This method helps train big language models better. It reduces the need for lots of training data and human annotation. That's often used in supervised and reinforcement learning.
- RLHF depends on human feedback and labels, which limits its scalability and may introduce human biases. In contrast, RLAIF employs AI-generated feedback based on constitutional principles. This change improves how well AI models work, making them more efficient and scalable. This ensures that models from OpenAI or Anthropic always act ethically and safely, following set standards
- RLAIF offers several advantages over RLHF. Large-scale AI applications, such as those by Microsoft or HuggingFace, require less human work and labeling. It is more scalable. RLAIF offers a complete learning experience. It adjusts AI models to meet ethical and safety standards. It also deals with problems like biases and harm in AI results.
- In RLAIF, the constitution is a guideline that helps generative AI models follow ethical and social standards. It is especially important in AI decision-making applications because there is potential for harm or unethical behavior. The constitution guides AI development to create an ethical feedback system. This is important for responsible AI governance in the changing AI landscape.