Announcing our Series C with $110M in total funding. Read more →.
Contents
Understanding RPA
Understanding IPA
IPA Vs. RPA: Key Differences
Considerations for Choosing Between IPA and RPA
Need for Intelligent Automation Strategy
How Does IA Incorporate RPA?
Real Time Adoption of IPA: Business Process Solutions
Top 7 Intelligent Automation Solutions
Implementation Best Practices
Conclusion
Encord Blog
Intelligent Process Automation Vs. Robotic Process Automation: Key Differences

Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Intelligent Process Automation (IPA) are software technologies that automate business processes to reduce human efforts and deliver maximum productivity to organizations.
RPA automates repetitive and manual processes such as opening email attachments, extracting data, filling out forms, etc. These tasks do not require complex decision-making per se.
On the other hand, IPA uses intelligent decision-making algorithms related to machine learning (ML), natural language processing (NLP), and other such areas to automate complex workflows requiring human intelligence.
According to a recent market report by Grand View Research, RPA's revenue share of the total cognitive process automation market size (~USD 4.87 billion) was 63% in 2022. Meanwhile, the IPA market is expected to grow 29.6% from 2023 to 2030.
In this article, we will learn about RPA and IPA, their key differences, and their applicability in the industry.
Understanding RPA
The main aim of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is to use software robots to automate frequently performed, time-consuming human actions. RPA is best suited for tedious tasks that require minimal decision-making, such as data entry, invoice processing, report generation, and customer data updates.
These tasks typically follow a rule-based approach and require little cognitive ability.
Benefits of RPA
- Increased Efficiency: RPA completes processes faster and more accurately, saving time and costs.
- Cost Savings: By reducing labor costs, RPA allows employees to focus on higher-value activities that require more cognition.
- Improved Accuracy: RPA eliminates the risk of human errors associated with manual data entry and repetitive tasks.
- Enhanced Scalability: RPA can easily scale to meet business needs and handle the increased workload.
- 24/7 Operations: Since RPA bots can work continuously, processes can be operated around the clock for fast turnaround times.
Limitations of RPA
- Limited Cognitive Capabilities: RPA can only perform tasks that adhere to strict rules and instructions—it cannot handle complex decision-making.
- Dependency on Structured Data: RPAs are not well suited to handle unstructured data such as free-form text, audio, or images.
- Integration Challenges: Integrating RPA with some legacy systems or applications can be challenging due to compatibility issues or data security concerns, as these systems may lack proper APIs or have strict access controls.
- Maintenance and Monitoring: RPA bots require periodic monitoring and updates, so organizations must allocate resources for troubleshooting and maintenance.
Unlike traditional automation, which often requires significant system changes, RPA works on top of existing applications, mimicking human actions. This makes RPA a more flexible and less disruptive automation solution.
Understanding IPA
Intelligent Process Automation (IPA) optimizes complex processes that require human-like cognitive capabilities beyond simple rule-based automation. IPA builds upon Robotic Process Automation (RPA) by incorporating artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms such as machine learning (ML) and NLP.
Unlike traditional automation, which relies on predefined rules, IPA systems can analyze data, derive insights, and adapt to make informed decisions in real-time.
Benefits of IPA
- Cognitive Capabilities: IPA systems can identify patterns, make data-driven decisions, and generate insights and analytics in real-time.
- Personalized Customer Experience: IPA systems can be tailored to customers' preferences, leading to greater satisfaction.
- Adaptive Learning: Unlike RPA, IPA systems continuously learn and adapt to changes, resulting in updated algorithms and decision-making strategies.
- Operational Efficiency: IPA systems improve performance, reduce costs, and minimize human interventions.
Limitations of IPA
- Implementation Complexity: IPA systems are resource-intensive. Money needs to be invested in skilled people in AI and appropriate computational environments.
- Ethical Considerations: When implementing IPA systems, organizations must comply with data privacy and security regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA.
- Scalability Issues: Scaling IPA systems is difficult due to certain infrastructure limitations, differences in governance frameworks, or organizational barriers.
- Data Quality: The unavailability of high-quality, structured data can result in poor or unreliable outcomes.
For example, in the healthcare industry, IPA can be used to analyze patient data, identify patterns, and provide personalized treatment recommendations, improving patient outcomes and reducing healthcare costs.
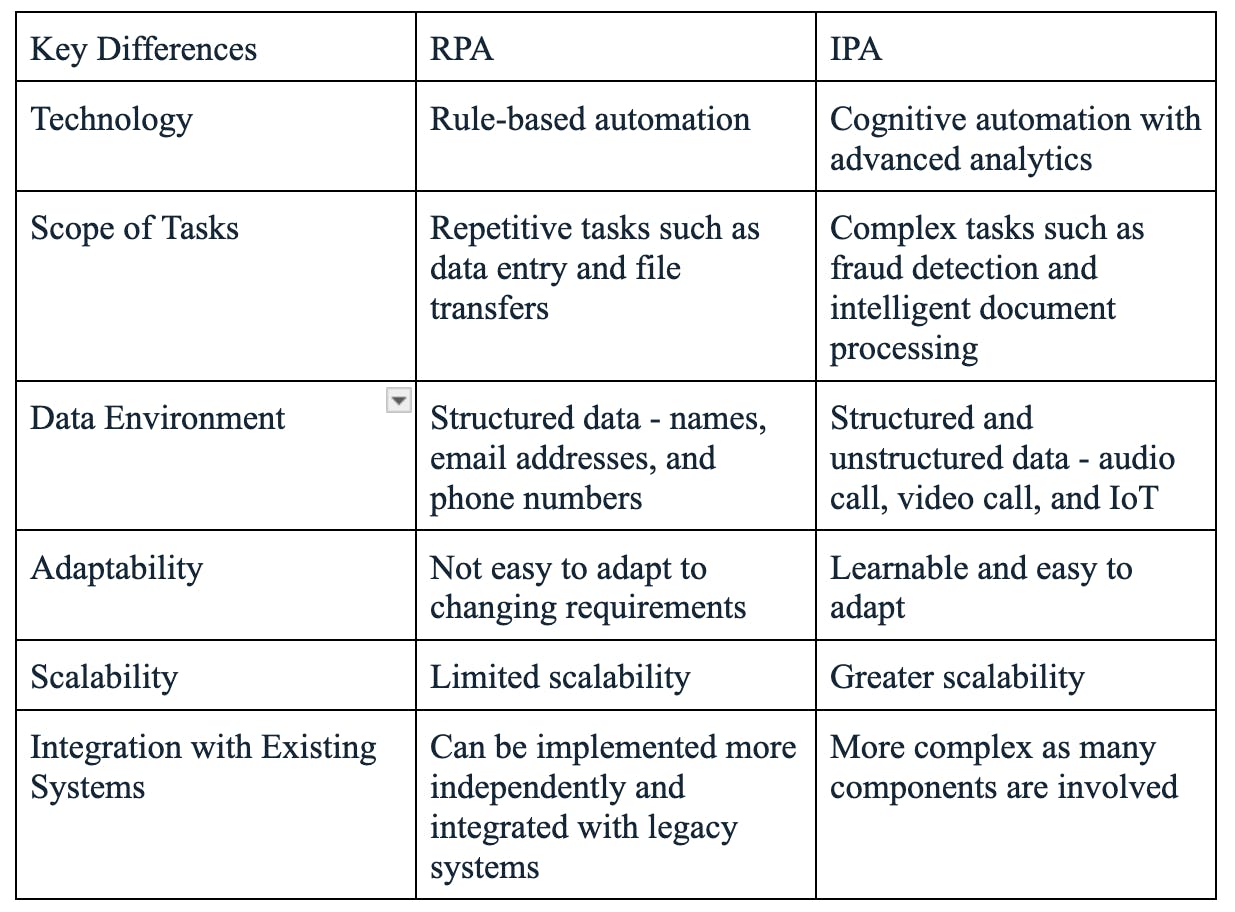
IPA Vs. RPA: Key Differences
As businesses explore automation solutions to improve efficiency and reduce costs, it's crucial to understand the differences between IPA and RPA. While both technologies aim to automate tasks, their capabilities, scope, and integration requirements differ. Let's dive into the key differences between IPA and RPA.

Technology Differences
RPA relies on rule-based automation, following predefined instructions to complete tasks. In contrast, IPA integrates AI technologies, enabling cognitive automation and advanced analytics. This allows IPA systems to learn, adapt, and make decisions based on data patterns and insights.
Scope of Tasks
RPA is well-suited for repetitive, rule-based tasks that require minimal decision-making, such as data entry, file transfers, and simple calculations. On the other hand, IPA can handle complex cognitive tasks that require problem-solving and decision-making capabilities, such as fraud detection, customer sentiment analysis, and intelligent document processing.
Data Environment
In a standardized format, RPA works best with structured data, such as names, email addresses, and phone numbers. However, IPA can handle structured and unstructured data, including audio calls, videos, and IoT data. This enables IPA to extract insights from a wider range of data sources and automate more diverse processes.
Adaptability
RPA systems are rule-bound and static, meaning they don't easily adapt to changing environments or requirements without manual intervention. In contrast, IPA systems are learnable and continuously improve through ML algorithms. This adaptability allows IPA to optimize processes and respond to evolving business needs.
For example, an IPA system in customer service can learn from past interactions to provide more personalized and efficient support over time.
Scalability
IPA offers greater scalability for handling complex tasks and large data volumes than RPA. As businesses grow and their automation needs expand, IPA's ability to learn and adapt makes it better suited to scale alongside the organization.
RPA may face limitations in certain applications due to its reliance on predefined rules and lack of cognitive capabilities.
Integration with Existing Systems
RPA systems can often be implemented more independently and integrated with legacy systems without significant modifications. However, IPA systems require seamless integration with AI technologies and diverse data sources to unlock their full potential.
This integration process may be more complex and time-consuming as it involves ensuring compatibility and data flow between various components of the IPA solution and existing enterprise systems.
Considerations for Choosing Between IPA and RPA
When deciding between Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Intelligent Process Automation (IPA), organizations must carefully evaluate several key factors to ensure their automation initiatives align with their strategic goals and objectives.
Businesses can make informed decisions and select the most appropriate automation solution for their needs by considering the following aspects.
- Nature of Tasks: If the tasks to be automated are primarily repetitive and rule-based, RPA may be sufficient. However, IPA may be more appropriate if the tasks involve deriving insights and analysis.
- Scope of Automation: If automation is required for specific tasks within a department or function, RPA is a better choice. IPA should be chosen if the goal is to automate and streamline complex cognitive tasks across multiple departments or functions.
- Integration with AI Technologies: IPA may be viable if the organization has the expertise and infrastructure to integrate AI technologies into automation initiatives. Otherwise, RPA may be a more practical choice.
- Data Availability: If the tasks involve structured, well-defined data sets, RPA may be sufficient. However, IPA may be necessary to analyze unstructured data, dynamic processes, or real-time insights.
- Regulatory and Compliance Considerations: Consider regulatory requirements and compliance standards that may impact automation initiatives. Ensure that chosen automation solutions adhere to data protection regulations, ethical guidelines, and industry standards, especially in sensitive healthcare, finance, and legal domains.
- Cost and ROI: Evaluate the costs of implementing and maintaining automation initiatives, including software licensing fees, infrastructure, and personnel expenses. Consider the potential ROI regarding efficiency gains, cost savings, productivity improvements, and strategic value.
For example, a financial institution looking to automate its customer onboarding process may choose IPA over RPA due to the need to analyze unstructured data from various sources, ensure compliance with stringent regulations, and the potential for significant ROI through improved customer experience and reduced processing times.
Need for Intelligent Automation Strategy
An Intelligent Automation (IA) strategy plays a crucial role in the growth and success of any organization. By aligning automation initiatives with overall business objectives, companies can leverage IA to reduce manual efforts, improve service quality, and drive strategic value. Here are the key reasons why an IA strategy is essential:
- Scalability: IA processes can easily scale to varying workloads, enabling organizations to handle increased demand without compromising accuracy or consistency
- Data Insights: IA can process large volumes of data and derive valuable insights, empowering organizations to make data-driven business decisions.
- Competitive Advantage: Organizations that adopt IA strategically can gain a competitive edge by delivering products and services faster, more accurately, and at a lower cost.
- Adaptability: IA enables organizations to quickly adapt to changing market trends and requirements, ensuring agility in a dynamic business environment.
- Compliance and Risk Management: Automation reduces the risk of errors that could lead to costly penalties or legal issues while maintaining compliance with regulations.
By developing a comprehensive IA strategy that considers the organization's goals, resources, and constraints, businesses can effectively harness the power of automation to drive growth, improve efficiency, and create lasting value.
How Does IA Incorporate RPA?
Intelligent Automation (IA) incorporates Robotic Process Automation (RPA) as its foundation, automating rule-based tasks. IA enhances RPA by integrating AI technologies like machine learning and natural language processing. This enables handling complex processes, unstructured data, intelligent decision-making, and adaptive automation.

Step by Step Process to achieve IPA
Real Time Adoption of IPA: Business Process Solutions
As businesses strive to stay competitive in today's fast-paced digital landscape, the real-time adoption of IPA has become crucial across various industries.
Using AI and RPA, organizations can streamline their processes, make data-driven decisions, and respond to changing market conditions in real-time. Let's explore two examples of how IPA is adopted in banking and e-commerce.
Fraud Detection in Banking
Banks and financial institutions use IPA to perform intelligent document processing, detect and prevent fraudulent activities in real-time. By combining AI-powered analytics with RPA capabilities, these organizations can monitor transactions, account activities, and user behaviors in real-time to identify suspicious patterns or anomalies.
For instance, if a credit card transaction deviates from a customer's typical spending patterns or occurs in a high-risk location, an IPA system can trigger immediate alerts or actions, such as blocking the transaction or notifying the customer. This real-time fraud detection helps banks mitigate financial losses and protect their customers' assets.
Dynamic Pricing in E-Commerce
E-commerce companies often use IPA to dynamically adjust prices based on real-time market conditions, competitor pricing, and customer behavior. By integrating AI algorithms with RPA bots, these companies can continuously monitor factors like demand, inventory levels, and competitor pricing in real time.
For example, if a competitor lowers their price for a particular product, an IPA solution can automatically adjust the prices of similar products to remain competitive, maximizing sales and profitability.
Additionally, IPA can leverage customer behavior data to personalize pricing and promotions, offering targeted discounts or bundled offers to increase customer engagement and loyalty.
Top 7 Intelligent Automation Solutions
- End-to-end success automation platform powered by Generative AI to accelerate automation development and team productivity.
- Streamlines enterprises' digital transformation by offering automation products across IT, finance, Customer Service, Sales, and HR departments.
- It offers a three-stage process to automation: discovering the highest-ROI opportunities for process optimization, seamless collaboration of people and systems with low-code development, and effective operation at a large scale.
- Provides features for continuous improvement, such as process mining, task mining, communications mining, and idea management.
Blue Prism Intelligent Automation Platform
- With strong client case studies such as Pfizer, which claims to have saved 500k hours of employees annually, Blue Prism is a competitive automation platform to accelerate growth and scale effectively.
- It offers features such as process development, automation, orchestration, and a Gen AI-powered IA platform.
- It is a comprehensive end-to-end cloud-based automation platform powered by AI that requires low code.
- Provides advanced AI features such as AI authoring, AI insights, AI processing, and AI generation.
IBM Robotic Process Automation
- It offers easy scaling and speeds up traditional RPA by providing AI insights to software robots so that they can finish tasks with no lag time.
- Provides features such as unattended, attended, and intelligent bots that work seamlessly with or without human intervention.
- SAP offers a low-code experience by combining RPA functionality, workflow management, decision management, process visibility, and AI capabilities on a single platform.
- Provides visual drag-and-drop tools for ease of use.
Pega Robotic Process Automation
- It allows digital transformation by bridging gaps between systems, speeding up processes, and eliminating outdated processes.
- Besides standard features of attended and unattended RPA, it also provides an auto-balancing feature to optimize robot resources and maximize the digital workforce.
Implementation Best Practices
The following are some of the best implementation practices for maximizing the benefits of implementing IPA and RPA strategies:
- Process Selection: Processes that are more repetitive, easy to automate, and deliver high value should be considered first for automation.
- Stakeholder Engagement: All the stakeholders affected by the automation should be involved in the development process. This will help ensure that automation aligns well with the organization's goals.
- Pilot Projects: The automation should first be tested on small pilot projects to understand its effectiveness, challenges, and modifications required before being used on a larger scale.
- Training and Upskilling: Comprehensive training and continuous upskilling of the people working with these strategies should be provided so that they can understand the trends of automation technologies and troubleshoot issues effectively.
- Robust Infrastructure: The organization must have a robust infrastructure supporting deploying RPA or IPA systems. This includes sufficient computing resources, good network connectivity, secure surroundings, and compatibility with existing systems.
- Security and Compliance: Measures should be implemented to protect sensitive data, ensure regulatory compliance, and mitigate automation-associated cybersecurity risks.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Automation solutions should be designed to be scalable and flexible enough to accommodate changes and allow ease of integration with other systems.
Conclusion
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Intelligent Process Automation (IPA) are transformative technologies built to revolutionize business process management. While RPA focuses on automating repetitive tasks, IPA takes automation to the next level by incorporating artificial intelligence and cognitive technologies for complex decision-making.
As the automation market evolves, organizations must carefully consider the scope, benefits, and challenges of RPA and IPA to determine which is best for their needs.
By adhering to implementation best practices, including process selection, stakeholder engagement, and robust infrastructure, businesses can maximize the benefits of automation while ensuring scalability, security, and compliance.
With the right approach, RPA and IPA will drive efficiency, agility, and competitiveness in this digital era.
Explore the platform
Data infrastructure for multimodal AI
Explore product
Frequently asked questions
The main challenges moving from RPA to intelligent automation include integrating AI technologies, managing data complexities, and upskilling teams for cognitive automation.
Regulatory concerns with RPA mainly revolve around data security, privacy, and accuracy, whereas with IPA, there are additional regulatory challenges related to algorithmic transparency, bias mitigation, and accountability for AI-driven decisions.
The four critical intelligent automation capabilities are AI integration, human-like decision-making, adaptive learning, and the provision of real-time analytics.
Determining the best automation software depends on the organization's specific business needs. UIPath is one of the best as it provides many solutions.
An intelligent automation platform is a software solution that combines RPA with AI technologies to automate processes and make decisions.
The top three RPA tools are UIPath, Automation Anywhere, and Blue Prism.
The steps of the automation journey typically include process assessment, pilot projects for validation, implementation, monitoring, and continuous service improvement.
To effectively implement intelligent automation, teams need training in AI technologies, process analysis, automation tools, change management, and compliance.
Encord ensures that annotation processes are aligned with team workflows through its integrated tools like the workflow builder. This feature allows teams to define specific tasks and responsibilities, facilitating collaboration and ensuring that all annotators are following the established guidelines and processes.
Yes, Encord offers a combined solution that includes both the annotation software tools and access to a trained workforce. This dual offering allows customers to choose the best fit for their needs, whether they prefer to manage annotations internally or outsource to our expert team.
Encord provides robust workflow management capabilities, allowing users to handle complex tasks with automation and project management features. This includes workflow assignments and user role scalability, which are essential for managing diverse teams and projects effectively.
Encord can enhance workflow management in robotics by providing a structured approach to defining and executing processes. This includes the ability to set up workflows for tasks such as new part introduction, ensuring that each step is clearly defined and efficiently executed.
Encord is designed to seamlessly integrate with existing human labeling workflows, providing a hybrid approach that combines automation and human oversight. This ensures that teams can enhance their efficiency while maintaining high standards of accuracy in data annotation.
Automation is a key feature of Encord's annotation process, allowing teams to speed up data labeling and reduce manual effort. By leveraging automated tools, Encord helps teams focus more on model development and less on time-consuming annotation tasks.
Yes, Encord incorporates automation within its data labeling framework, allowing teams to streamline their workflows. This advancement not only speeds up the labeling process but also minimizes human error, ensuring higher quality annotations.
Encord provides a comprehensive solution for data operations, integrating seamlessly with various tools to enhance your workflow. This includes compatibility with existing systems and the ability to manage large datasets effectively.
Encord includes automation capabilities that assist users in managing their annotation workflows. These features are designed to integrate with users' existing models, enabling them to build and refine their models more effectively.