Announcing our Series C with $110M in total funding. Read more →.
Contents
What is OCR?
What Does OCR Mean for PDFs?
Benefits of OCR
How Does OCR Work?
OCR Use Cases
OCR Challenges
Encord for Converting PDF with OCR
PDF OCR: Key Takeaways
Encord Blog
PDF OCR: Converting PDFs into Searchable Text
5 min read

Around 80% of information consists of unstructured data, including PDF documents and text files. The increasing data volume requires optimal tools and techniques for efficient document management and operational efficiency.
However, extracting text from PDFs is challenging due to different document layouts, structures, and languages. In particular, data extraction from scanned PDF images requires more sophisticated methods, as the text in such documents is not searchable.
PDF Optical Character Recognition (OCR) technology is one popular solution for quickly parsing the contents of scanned documents. It allows users to implement robust extraction pipelines with artificial intelligence (AI) to boost accuracy.
In this post, we will discuss OCR, its benefits, types, workings, use cases, challenges, and how Encord can help streamline OCR workflows.
What is OCR?
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) is a technology that converts text from scanned documents or images into machine-readable and editable formats. It analyzes character patterns and transforms them into editable text. The technique makes the document’s or image’s contents accessible for search, analysis, and integration with other workflows.
Users can leverage OCR’s capabilities to digitize and preserve physical records, enhance searchability, and automate data extraction. It optimizes operations in multiple industries, such as legal, healthcare, and finance, by boosting productivity, reducing manual labor, and supporting digital transformation.
What Does OCR Mean for PDFs?
OCR technology helps transform image-based or scanned PDF documents into machine-readable and searchable PDF files. PDFs created through scanning often store content as static images, preventing users from editing or searching within these documents. OCR recognizes the characters in these scanned images and converts them into selectable text.
The feature lets users edit PDF text, perform keyword searches, and simplify data retrieval using any PDF tool. For businesses and researchers, OCR-integrated PDFs streamline workflows, improve accessibility, and facilitate compliance with digital documentation standards.
It also means that OCR tools are critical to modern document management and archiving. They allow organizations to extract text from critical files intelligently and derive valuable insights for strategic decision-making.
Benefits of OCR
As organizations increasingly rely on scanned PDFs to store critical information, the demand for OCR processes to make PDF text searchable will continue to grow. Below are some key advantages businesses can unlock by integrating PDF OCR software into their operations.
- Better Searchability: OCR converts scanned or image-based PDFs into searchable text, allowing users to locate specific information instantly with standard PDF readers. This capability is especially useful for large document repositories.
- Faster Data Extraction and Analysis: OCR automates information retrieval from unstructured documents, enabling quick extraction of critical data such as names, dates, and figures. This facilitates real-time analysis and integration with decision-making tools.
- Cost Savings: Automating document digitization and processing reduces the need for manual data entry and storage of physical files. This minimizes labor costs and increases profitability.
- High Conversion Accuracy and Precision: Converting scanned PDFs directly into Word documents or PowerPoint presentations often leads to errors and misaligned structures. With OCR-powered tools, users can efficiently convert searchable PDFs into their desired formats with PDF converters, ensuring accuracy and precision in the output.
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Digitized and organized documents help organizations meet compliance requirements. OCR ensures fast retrieval of records during audits and legal inquiries.
- Scalability: Whether processing hundreds or millions of documents, OCR scales effortlessly to handle enterprise-level demands.
- Integrability with AI Systems: OCR-generated data can feed into AI models for natural language processing, analytics, and automation. The functionality enhances broader business intelligence capabilities and customer experience.
How Does OCR Work?
OCR comprises multiple stages to convert scanned or image-based PDFs into machine-readable text. Here's a breakdown of the process:
Image Acquisition
The process begins with acquiring a digital image of the document through scanning, photography, or capturing an image from a PDF. The image can be in a standard JPG or PNG format. The quality and resolution of this image are critical for accurate OCR performance.
Preprocessing
Preprocessing improves image quality for better text recognition. Common techniques include:
- Noise Removal: Eliminating specks, smudges, or background patterns.
- Deskewing: Correcting tilted or misaligned text.
- Binarization: Converting the image into a binary format (black and white) for easier character recognition.
- Contrast Enhancement: Adjusting brightness and contrast for clear text.
Text Recognition
This is the core phase of OCR and uses three key techniques:
- Pattern Matching: Comparing detected shapes with stored templates of known characters.
- Feature Extraction: Identifying features like curves, lines, and intersections to decode characters.
- Layout Recognition: Analyzing the document structure, including columns, tables, and paragraphs, to retain the original formatting.
Post Processing
Postprocessing refines the output by correcting errors using language models or dictionaries and ensuring proper formatting.
This step often includes spell-checking, layout adjustments, and exporting to desired formats like Word or Excel. It may require using PDF editors like Adobe Acrobat to adjust inconsistencies in the converted files.
Types of OCR
OCR technology caters to diverse use cases, leading to different types of OCR systems based on functionality and complexity. The sections below highlight four OCR types.
Simple OCR
Simple OCR uses basic pattern-matching techniques to recognize text in scanned images and convert them into editable digital formats.
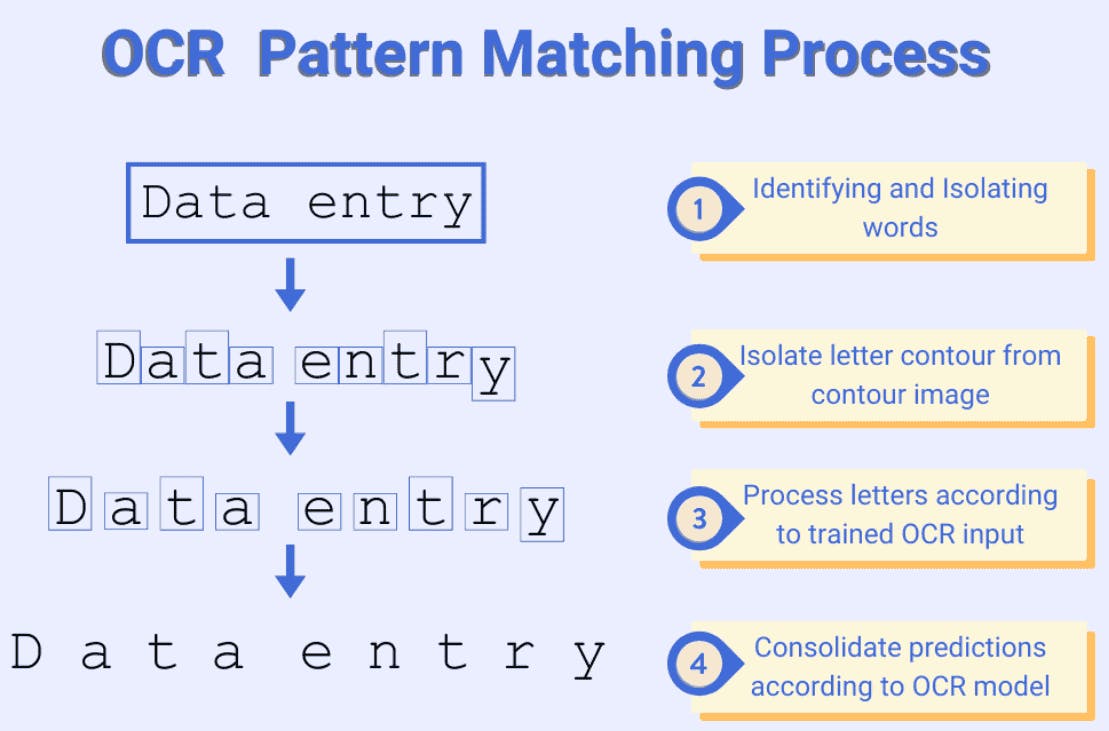
While effective for clean, well-structured file formats, it struggles with complex layouts, handwriting, or stylized fonts. It is ideal for straightforward text conversion tasks like digitizing printed books or reports.
Intelligent Character Recognition (ICR)
ICR is an advanced form of OCR designed to recognize handwritten characters. It uses machine learning (ML) and neural networks to adapt to different handwriting styles, providing higher accuracy.

ICR detecting the word “Handwriting”
It helps process forms, checks, and handwritten applications. However, accuracy may still vary depending on handwriting quality and file size.
Optical Mark Recognition (OMR)
OMR identifies marks or symbols on predefined forms, such as bubbles or checkboxes. It helps in applications like grading tests, surveys, and election ballots.

OMR Scanner recognizing marked checkboxes
OMR requires structured forms with precise alignment and predefined layouts for accurate detection.
Intelligent Word Recognition (IWR)
Intelligent Word Recognition (IWR) identifies entire words as cohesive units rather than breaking them down into individual characters. This approach makes it particularly effective for processing cursive handwriting and variable fonts.

IWR Recognizing Cursive Handwriting
Unlike Intelligent Character Recognition (ICR), which focuses on recognizing characters one at a time, IWR analyzes the complete word image in a single step. The approach enables faster and more context-aware recognition.
It is helpful in scenarios where context-based recognition is essential, such as signature verification or handwritten document digitization.
OCR Use Cases
OCR's versatility and cost-effectiveness drive its rapid adoption across various industries as businesses use it to streamline everyday operations. The list below showcases some of the most prominent OCR applications in key sectors today.
Legal and Finance
OCR refines knowledge management in legal and financial sectors by digitizing critical documents. It automates contract analysis, extracting clauses, dates, and terms for faster review.
In addition, the technology simplifies invoice processing in finance. It captures data like amounts and vendor details for seamless accounting.
It also enables e-discovery in legal cases by making scanned documents searchable. The technique ensures compliance by organizing records for quick retrieval during audits.
Healthcare
The healthcare industry improves document management with OCR by digitizing patient records, prescriptions, and insurance claims for quick retrieval and processing.
It enables accurate extraction of critical data from medical forms, speeding up billing processes and reducing errors.
OCR also aids in converting historical records into searchable digital formats. The approach enhances research efforts by allowing professionals to manage large volumes of healthcare documentation.
Education
Teachers and students can use OCR to digitize textbooks, lecture notes, and research materials to make them searchable and easily accessible. OCR also helps in administrative tasks like processing student applications and transcripts.
It allows instructors to preserve historical documents and convert them into digital editable formats. Moreover, OCR enhances study material accessibility by transforming them into formats suitable for students from different backgrounds.
For example, teachers can integrate OCR with AI-powered translation software. They can use it to translate scanned PDF documents in French and German into English or other local languages, allowing for multilingual learning.
Government and Public Sector
OCR improves government and public sector operations by digitizing records, including birth certificates, tax forms, and land registries, for quick access and retrieval.
It automates data extraction from citizen applications and forms, reducing manual workloads. OCR also supports transparency by making public documents searchable and accessible through official government websites.
Retail and E-Commerce
OCR contributes to retail and e-commerce by automating invoice processing, inventory management, and order tracking. It extracts key product details from receipts and invoices, ensuring accuracy and relevance in accounting procedures.
OCR also enables quick integration of scanned product labels and packaging data into digital systems. This allows retailers to use the data for better catalog management and sales tracking.
Additionally, it supports customer service by converting forms, feedback, and returns into searchable and manageable digital formats.
Logistics
OCR improves logistics efficiency by automating data extraction from shipping labels, invoices, and customs documents. It optimizes inventory management and tracking by converting physical records into digital formats.
The method also speeds up delivery forms and bills of lading processes, reducing manual data entry. This enhances accuracy, boosts operational efficiency, and supports real-time tracking across the supply chain.
Media and Publishing
In media and publishing, OCR transforms printed materials like newspapers, books, and magazines into searchable and accessible digital formats. It simplifies content archiving, allowing users to retrieve articles and historical publications quickly.
The technology also aids in converting manuscripts into digital formats for editing and publishing. Efficiently indexing large volumes of content helps improve the speed and accuracy of editorial workflows.
Travel and Transportation
The travel and transportation industry uses OCR to automate data extraction from documents like boarding passes, tickets, and passports, enhancing check-in efficiency and reducing errors. It simplifies booking and reservation systems by converting paper forms into digital formats.
Additionally, OCR improves transportation management by digitizing vehicle records, driver licenses, and shipping documents. This improves accuracy, efficiency, and overall customer service.
OCR Challenges
Despite its many advantages, OCR technology faces several challenges that can limit its effectiveness in specific applications. These include:
- Accuracy: OCR accuracy heavily depends on the quality of input documents. Poor scan resolution, faded text, and noisy backgrounds often lead to recognition errors and reduce output reliability.
- Language Diversity: OCR systems may struggle to support multiple languages, especially those with complex scripts or right-to-left text orientation. While advanced tools address this, lesser-used languages often face limited support.
- Document Structure: OCR struggles with maintaining the formatting and layout of complex documents containing tables, columns, or graphics. This can result in misaligned or missing content, especially in documents with intricate designs.
- Computational Resources: High-quality OCR processing requires significant computational resources, particularly for large volumes or complex layouts. This can pose challenges for organizations with limited technical infrastructure.
- Lacks Contextual and Semantic Understanding: While OCR excels at recognizing characters, it cannot interpret context or semantics. This limitation affects tasks requiring comprehension, such as extracting meaning from ambiguous text or interpreting handwriting nuances.
- Data Security and Privacy: Processing sensitive documents with OCR, especially on cloud-based platforms, raises privacy and compliance concerns. Ensuring secure processing environments is critical for protecting sensitive information.
Encord for Converting PDF with OCR
The challenges mentioned above can hamper a user’s ability to leverage OCR’s capabilities to get a clean and accurate editable PDF. Although multiple online tools offer OCR functionality, they can fall short of the features required for building scalable PDF text extraction systems.
Alternatively, enterprises can build customized solutions using open-source libraries for specific use cases. However, the development may require significant programming and engineering expertise to create a robust and secure document management platform.
As industries embrace greater digitization, organizations must invest in more integrated solutions that combine advanced OCR capabilities with AI-driven functionality. One such option is Encord, an end-to-end AI-based data curation, annotation, and validation platform with advanced OCR features.
Encord can help you build intelligent extraction pipelines to analyze textual data from any document type, including scanned PDFs. It is compatible with Windows, Mac, and Linux.

Key Features
- Document Conversion: Encord lets you quickly convert scanned PDFs into editable documents through OCR. You can easily adjust the converted files further using tools like Acrobat Pro, Google Docs, or Microsoft Word.
- Curate Large Datasets: It helps you curate and explore large volumes of text through metadata-based granular filtering and natural language search features. Encord can handle various document types and organize them according to their contents. The ability leads to better contextual understanding when parsing text from image-based PDFs.
- Multimodal Support: Encord is a fully integrated multimodal framework that can help you integrate text recognition pipelines with other modalities, such as audio, images, videos, and DICOM. This will help you convert PDFs with complex layouts and visuals more accurately.
- Data Security: The platform complies with major regulatory frameworks, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), System and Organization Controls 2 (SOC 2 Type 1), AICPA SOC, and Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) standards. It also uses advanced encryption protocols to protect data privacy.
G2 Review
Encord has a rating of 4.8/5 based on 60 reviews. Users highlight the tool’s simplicity, intuitive interface, and several annotation options as its most significant benefits.
However, they suggest a few areas for improvement, including more customization options for tool settings and faster model-assisted labeling.
Overall, Encord’s ease of setup and quick return on investments make it popular among AI experts.
PDF OCR: Key Takeaways
Businesses are transforming OCR from a standalone tool for converting scanned images into text and turning them into a key component of AI-driven applications. They now use OCR to extract text and build scalable solutions for natural language processing (NLP) and generative AI frameworks.
Below are a few key points regarding OCR:
- OCR and PDFs: Users leverage OCR to convert scanned PDF images into searchable documents. The functionality helps them optimize document management and analyze textual data for more insights.
- OCR Challenges: Poor image quality and different layouts, structures, and contextual design make it difficult for OCRs to read text from scanned PDFs accurately.
- Encord for OCR: Encord’s powerful AI-based data extraction and state-of-the-art (SOTA) OCR features can help you analyze complex image-based PDFs instantly.
Explore the platform
Data infrastructure for multimodal AI
Explore product
Frequently asked questions
OCR converts scanned documents, images, or PDFs into machine-readable and editable text.
PDFs can be in the form of images created by scanning physical documents, which lack embedded text layers needed for searchability.
You can use online converters to extract and convert the text into an editable Word format.
Popular options include Encord, Adobe Acrobat, and Smallpdf to extract data into Excel format.
Tools like Google Drive, Free Online OCR, and PDF24 offer free OCR functionality to make PDFs searchable.
Encord offers capabilities to assist with curating data, including images, OCR, and PDFs, which can enhance your data sampling and curation efforts. This is particularly useful for managing large volumes of documents and ensuring that relevant insights can be extracted efficiently.
Encord converts PDF files into images to facilitate optical character recognition (OCR). This approach allows for effective annotation and data extraction from documents that are often received as images, ensuring a streamlined workflow for document verification.
Encord ensures OCR accuracy by running multiple models in parallel and maintaining a ground truth for validation. This system is complemented by human oversight, which helps verify results and mitigates potential inaccuracies generated by large language models.
Encord offers advanced annotation features that include Optical Character Recognition (OCR) for extracting text from images and documents. These capabilities enhance the ability to structure and index data effectively, making it accessible for users.
Encord utilizes OCR models within its labeling platform to automatically extract text from both printed and handwritten documents. This feature helps streamline the annotation process by pulling relevant text directly from the selected areas.
Yes, Encord supports annotation for both PDFs and image formats. By converting PDFs to images, the platform leverages OCR technology to enable efficient data extraction and annotation across different document types.
Encord enhances annotation speed by integrating OCR models that automatically extract and annotate text, allowing users to focus on reviewing and refining the annotations rather than performing manual text entry.
Yes, Encord is designed to handle documents that contain both printed text and handwritten notes, making it suitable for various types of data, including clinical reports and educational materials.