Announcing our Series C with $110M in total funding. Read more →.
Contents
ITK-Snap
ITK-Snap Alternatives
#1 Encord
#2 MITK Workbench
#3 OsiriX
#4 3D Slicer
#5 HOROS
#6 OHIF
#7 CVAT
#8 MONAI
ITK-Snap Alternatives: Key Takeaways
Encord Blog
Top 8 ITK-Snap Alternatives in 2024
The medical imaging industry is rapidly advancing to address emerging global health challenges, including an increasing prevalence of chronic illnesses, a rise in the elderly population, and a move towards non-invasive procedures. The evolving trend is evident in a recent report that predicts the imaging technology market will be worth $54.47 billion by 2028, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.1%.
The primary driver of such growth is the recent surge in innovative imaging tools for managing complex healthcare data. ITK-Snap is one such innovation, attracting an impressive user base because of its open-source framework and flat learning curve.
However, the software focuses mainly on image segmentation. It also lacks scalability, collaborative features, and automation to handle modern medical tasks with complex Wimage formats and extensive data volumes.
Due to its limitations, we discuss the top eight (8) alternatives to ITK-Snap, as mentioned below. The list will help you find the most suitable imaging tool to streamline your medical workflows and boost productivity.
- Encord
- 3D Slicer
- HOROS
- OsiriX
- OHIF Viewer
- MONAI
- CVAT
- MITK Workbench
ITK-Snap
ITK-Snap is a multi-platform, open-source medical imaging tool for segmenting 3D and 4D medical images. It was developed by researchers at the University of Pennsylvania under Paul Yushkevich's leadership. It supports the Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM) and Neuroimaging Informatics Technology Initiative (NIfTI) file formats.
It features manual segmentation tools that let you assign segmentation labels to each voxel and offers semi-automatic segmentation through active contours.
Challenges of Using ITK-Snap
Although ITK-snap is an easy-to-use imaging platform with precise segmentation results, it has several drawbacks for enterprise-scale dynamic projects. The list below mentions a few of these challenges:
- Lack of Fully Automated Segmentation: Semi-automatic segmentation requires users to manually define relevant parameters. While it is faster than manual segmentation, the method (e.g., Snake Interaction Mode) can become cumbersome when dealing with large and complex imaging datasets.
- No Advanced Functionality: The tool focuses mainly on medical image segmentation tasks and does not provide other essential features such as multiplanar reconstruction (MPR), image fusion, volume rendering, and integration with the Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS).
- Lack of Collaboration Tools: The platform does not offer tools for creating shared workflows and collaborating between team members.
- Data Security and Compliance Certifications: ITK-snap does not comply with data security standards required by the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), System and Organization Controls 2 (SOC 2), and International Organization for Standardization 27001 (ISO 27001).
Due to these limitations, ITK-snap becomes inefficient for large-scale medical image processing containing sensitive patient information.
So, let’s move on to the next section to discuss a few viable alternatives to ITK-snap.
ITK-Snap Alternatives
Due to technological advancements, interconnected systems, new diseases, and changing demographics, the healthcare ecosystem system is becoming increasingly complex. This trend calls for a scalable imaging solution with robust security protocols. It must also include:
- Collaboration tools.
- Intuitive user interface (UI).
- Integration with existing technology stacks.
- Automation.
- Other advanced features to manage complex medical data.
With ITK-snap posing the challenges mentioned above, the list below provides an overview of alternative tools ranked according to these factors.
#1 Encord
Encord Annotate is an end-to-end data-centric AI platform for managing DICOM (and NIfTI) data at any scale and for teams of all sizes. It includes basic and advanced features for annotating and segmenting medical images to build AI models. It also integrates natively with other tools on the Encord platform:
- Index for managing and curating data.
- Active for evaluating and validating your machine learning (ML) models.
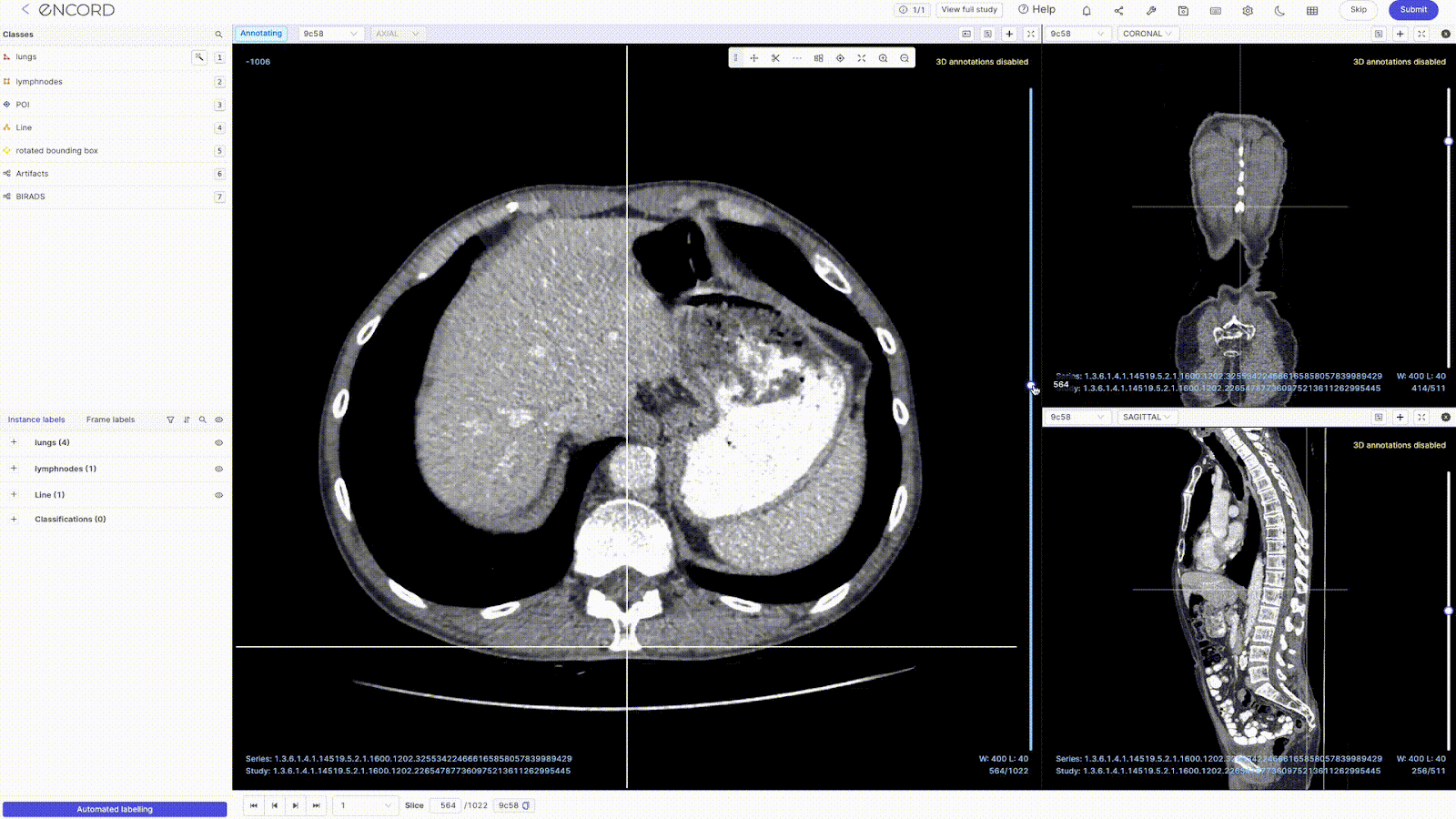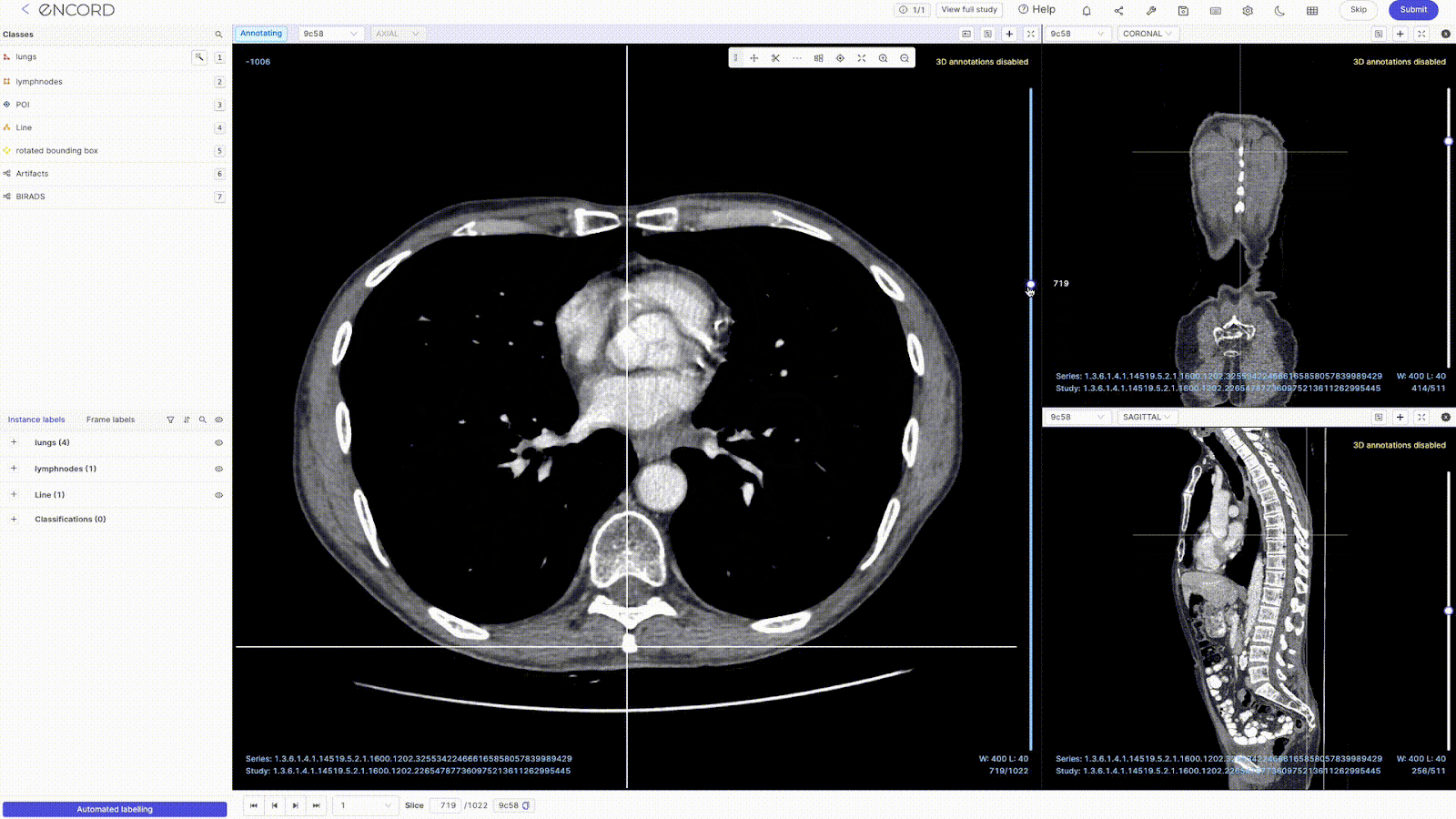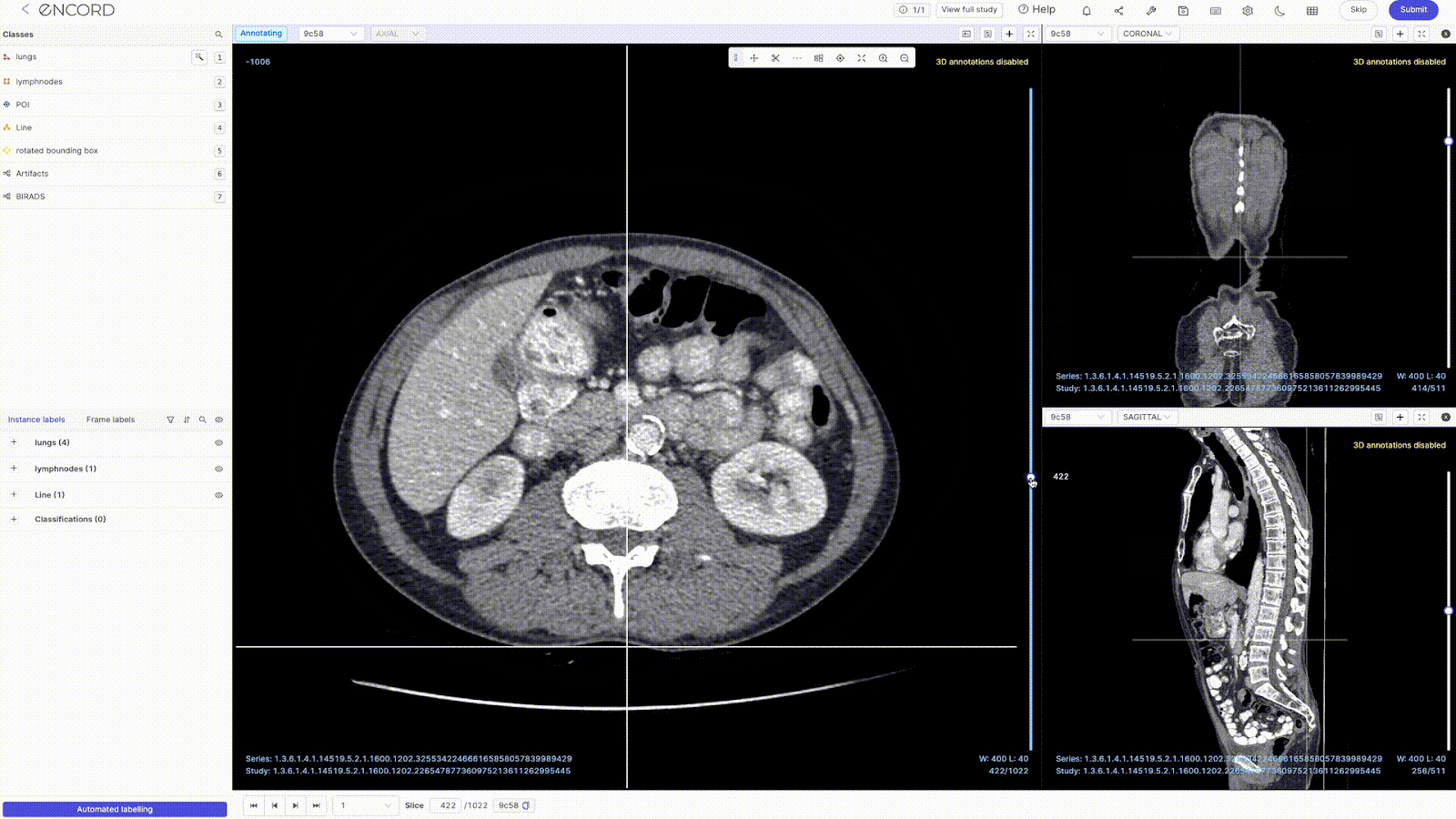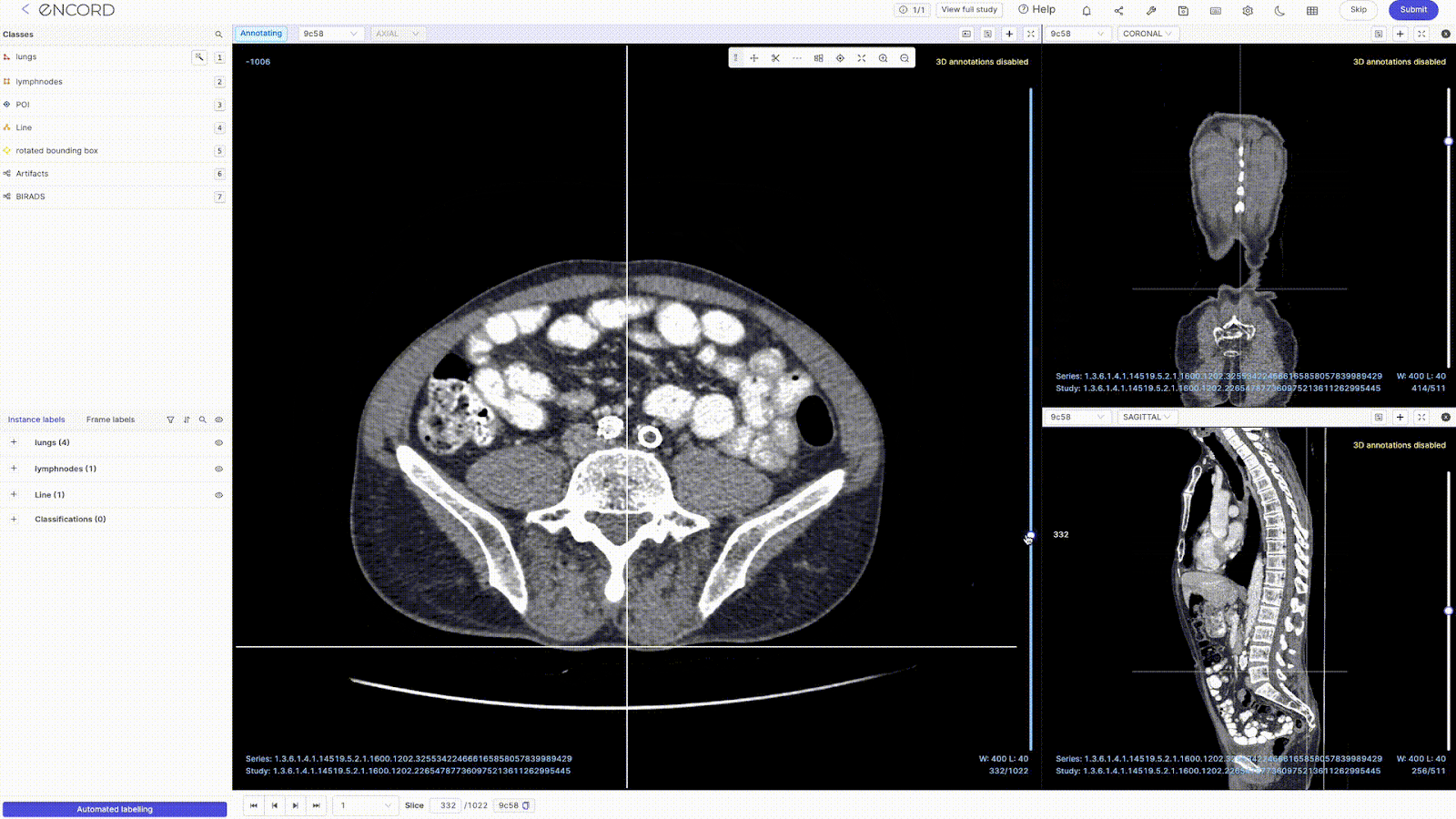
Key Features
- Fully-Automated Labeling (Segmentation): The platform speeds up the annotation with fully automated segmentation features, including:
- - Segment Anything Model (SAM) Integration to automatically create labels around distinct features in all supported file formats (DICOM: CT, X-ray, and MRI).
- - Interpolation to auto-create instance labels by estimating where labels should be created in videos and image sequences.
- - Import custom model predictions through Encord’s SDK or API to automatically pre-segment your images and save on annotation costs.
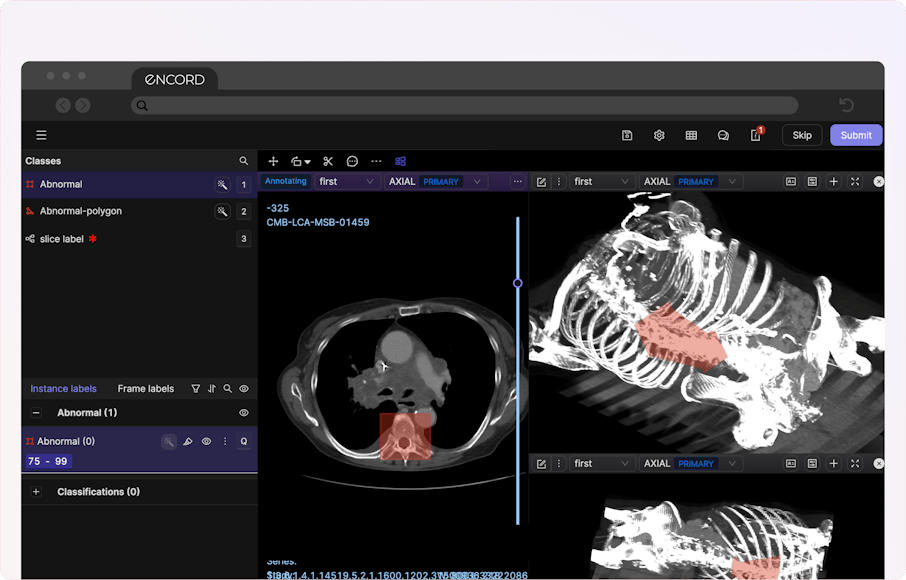
- 2D Multiplanar Reconstruction (MPR): Encord's MPR display lets you reconstruct cross-sectional scans into 2D orthogonal images (coronal, sagittal, and axial views) for efficient annotation and visualization. You can also transform all the reconstructed views into detailed 3D renderings that prominently display your annotations.
- Maximum Intensity Projection (MIP): The DICOM Editor supports MIP mode for a 3D view of CT scans. You can switch MIP on/off for each view—changing the slab thickness (ST) to something greater than 0 enables MIP mode.
- Collaboration: Encord Annotate lets you create an organization for shared projects defined based on datasets and team members. To manage tasks at different stages, you can create workflows and assign relevant team members roles. User roles include admin, team member, reviewer, and annotator.
- Data Security: Encord Annotate complies with major compliance frameworks, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), System and Organization Controls 2 (SOC 2 Type 1), AICPA SOC, and Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) standards. It also uses advanced encryption protocols to protect data privacy.
- Scalability: The platform allows you to upload up to 500,000 images (recommended), 100 GB in size, and 5 million labels per project. You can also upload up to 200,000 frames per video (2 hours at 30 frames per second) for each project. The documentation provides more guidelines for scalability.
- Easy-to-Use UI: The tool offers an intuitive, easy-to-navigate user interface (UI) with clearly marked panels and a powerful search capability. This helps users with no prior expertise set up a project quickly. It also provides an SDK for labeling and managing annotation projects.
- Integration: To import datasets, integrate popular cloud storage platforms, such as AWS, Google Cloud, Azure, and Open Telekom Cloud OSS.
Other Features
- Pixel Intensity: Since Encord Annotate natively renders DICOM files, the platform can display images with full intensity values exceeding 20,000 pixels.
- Supported Annotation Types: The platform supports bounding boxes, polygons, polylines, bitmask segmentation, frame classification, and keypoint annotation.
- Supported Modalities: Encord Annotate supports multiple medical image modalities, including Computed Tomography (CT), X-ray, and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scans.
- Other Displays: The DICOM Editor also supports displays like multiple series viewing, window width (WW) and window level (WL), hanging protocols, and metadata view.
Best for
- Healthcare professionals looking for an enterprise-grade DICOM solution to process large-scale image data.
Pricing
- Encord has a pay-per-user pricing model with Starter, Team, and Enterprise options.
#2 MITK Workbench
The Medical Imaging Interaction Toolkit (MITK) is based on the Insight Toolkit (ITK) and Visualization Toolkit (VTK). It offers registration and segmentation features with advanced visualization functionality while supporting high-level interactions to construct and modify data objects.

Key Features
- User Interface: It has an easy-to-use interface with a simple design displaying all the relevant tools on a single screen.
- Integrability: MITK integrates with multiple plugins, including Chili, a PACS module.
Other Features
- Geometry Information: The platform provides accurate information regarding an object’s position, area, and volume to help you handle 3D data.
- Arbitrary Rendering: MITK renders objects with properties of arbitrary type and lets you configure them for a specific renderer.
Best for
- Teams looking for a cost-effective development toolkit to develop a basic customized visualization solution for image analysis.
Pricing
- MITK is open-source.
#3 OsiriX
OsiriX is a Mac-based solution that reads DICOM files in multiple formats and offers advanced post-processing features for 2D and 3D images. It also provides a multilingual interface in more than ten languages.

Key Features
- Collaboration: Osirix lets you share reports using built-in database-sharing features and retrieve studies from other DICOM software.
- User Interface: It has an easy-to-use interactive UI.
- Integrability: The tool connects with PACS.
Other Features
- Friendly for 3D-Printer: OsiriX lets you export 3D images in STL format for 3D printing.
- Image Fusion: It supports positron emission tomography (PET-CT), PET-MR, and single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT-CT) image fusion.
Best for
- Teams looking for a solution to process 3D image files on MacOS.
Pricing
- OsiriX has fixed monthly subscription-based pricing for a single user.
#4 3D Slicer
3D Slicer is an open-source software compatible with Windows, Linux, and MacOS that lets you view, process, segment, register, and analyze medical images.

Key Features
- Integrability: 3D Slicer integrates with PACS using DICOMweb.
- Automation: The tool uses the NVIDIA AI-assisted segmentation extension. It consists of algorithms to segment anatomical structures automatically. Users can also benefit from the DeepInfer extension, which lets them deploy pre-trained deep learning models for image analysis.
- Virtual and Augmented Reality (VR & AR): 3D Slicer supports virtual and augmented reality (VR & AR) visualizations with HTC Hive, Windows mixed reality headsets, and Oculus Rift using the SlicerVR extension.
Other Features
- Volume Rendering: The platform allows 3D rendering of medical images such as CT and MRI scans.
- 3D Markups: The tool lets you use multiple markups to define regions of interest in 3D medical images.
Best for
- Teams looking for a 3D-printer-friendly DICOM solution with advanced visualization features.
Pricing
- 3D Slicer is open-source.
#5 HOROS
HOROS is a basic DICOM image viewer that is only compatible with MacOS.

Key Features
- Data Security: HOROS complies with GDPR standards.
- Collaboration: The tool lets you quickly share studies with team members, who can download them directly from the HOROS cloud.
- Integrability: The platform integrates with PACS.
Other Features
- Multiplanar Reconstruction (MPR): HOROS supports MPR, allowing you to view medical images in axial, coronal, and sagittal planes.
- Maximum Intensity Projection (MIP): It also supports MIP for a 3D view of CT scans.
Best for
- Teams looking for a Mac-based solution for quickly viewing medical images.
Pricing
- Horos is open-source.
#6 OHIF
Open Health Imaging Foundation (OHIF) is a web-based, open-source imaging solution to view, annotate, and segment medical images. It requires no additional installation and offers intuitive visualizations for an in-depth image analysis.

Key Features
- User Interface: OHIF has a user-friendly and interactive UI.
- Flexible Visualizations: The tool supports MPR and image fusion.
- Measurement and Annotation: It features length, bidirectional, annotation, ellipse, and calibration tools to analyze complex anatomical structures.
Other Features
- 3D Segmentation: OHIF allows you to segment 3D anatomical structures.
- Customizable Workflows: The tool features a plug-in framework to design custom workflows tailored to your use case.
Best for
- Teams looking for a beginner-level and high-speed imaging solution.
Pricing
- The tool is open-source.
#7 CVAT
The Computer Vision Annotation Tool (CVAT) is a general-purpose annotation solution to label images and videos. It supports annotation for classification, detection, and segmentation tasks.

Key Features
- Scalability: The CVAT Cloud version allows you to scale your projects depending on your requirements and frees you from active infrastructure management.
- Data Security: It complies with GDPR standards and offers end-to-end encryption with regular security audits.
- Collaboration: The CVAT platform lets you create projects and assign relevant user roles to control the annotation workflow at different stages.
- Automation: The tool features built-in deep learning models to label images automatically.
Other Features
- Supported Annotation Types: The platform supports bounding boxes, polylines, polygons, key points, cuboids, and segmentation masks.
- Performance Analytics: CVAT allows you to monitor annotation performance through multiple metrics, including annotator work hours and objects labeled per hour.
Best For
- Teams looking for a cost-effective labeling solution to develop computer vision systems for medical use cases.
Pricing
- CVAT offers a free, Solo, and Team versions.
#8 MONAI
The Medical Open Network for Artificial Intelligence (MONAI) is an open-source project providing an end-to-end framework for building advanced AI models for medical use cases. It consists of MONAI Label, Care, and Deploy modules to annotate, train, and deploy models.

Key Features
- Integrability: MONAI label integrates with PACS through DICOMWeb. It also integrates with CVAT, OHIF, and 3D Slicer to view and annotate medical image files.
- Automation: Researchers working in endoscopy can benefit from active learning techniques to streamline the annotation workflow.
- Supported Models: MONAI features the latest segmentation models for segmenting anatomical structures such as the brain, spleen, and lungs.
Other Features
- Supported Modalities: MONAI label supports CT and MRI scans, pathological images, and endoscopy videos.
- Customizable Design: The platform offers app customization to suit specific use cases.
Best for
- Researchers looking for a platform to build and deploy medical-specific AI models.
Pricing
- MONAI is open-source.
ITK-Snap Alternatives: Key Takeaways
With the ever-increasing volume and variety of data in the medical domain, investing in a cost-effective, scalable, and versatile imaging solution is becoming a necessity. Below are a few key points to remember regarding medical imaging tools.
- Critical functionalities to look for: Scalability, security, and collaboration are the top factors when investing in an imaging platform.
- Limitations of ITK-Snap: While ITK-Snap is an efficient segmentation tool, it lacks the key features to make it suitable for an enterprise-grade and highly dynamic system.
- Alternatives to ITK-Snap: Encord, OsiriX, and 3D Slicer are suitable alternatives.
Explore the platform
Data infrastructure for multimodal AI
Explore product
Frequently asked questions
Image segmentation involves breaking a medical image into relevant segments to highlight regions of interest.
Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM) is a standard protocol for storing and sharing medical images across multiple healthcare systems.
Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS)is the backend hardware and software for transmitting medical information between medical devices.
3D Slicer, MITK, and OHIF are primary open-source tools for annotating medical images.
Encord, 3D Slicer, and MITK, are user-friendly alternatives for 3D segmentation tasks.
Yes. 3D Slicer and MITK can integrate with PACS. OsiriX can integrate with the radiology information system.
A 64-bit system with 4 GB of memory is required as a minimum to process large files.
Encord provides significant benefits over offline tools, including enhanced collaboration features, real-time access to annotations, and streamlined workflow management. The online platform allows for better distribution of annotation tasks, ensuring that teams can work more efficiently together.
Encord offers various integration options, including support for cloud storage solutions like Google Cloud Platform (GCP). Users can seamlessly connect their existing data stores to the Encord platform, facilitating efficient data management without the need to migrate all data to a new location.
Users can integrate their data into Encord through a private cloud setup or by directly uploading data using the fully supported Python SDK. For those planning to scale, Encord also supports integrations with Google Cloud Platform, which is a common choice among customers.
For uploading large data sets, it's recommended to send the data to Encord, and the team will upload it for you using the SDK. Managing large uploads via the user interface can be less efficient, so utilizing programmatic methods is preferred for bulk data transfers.
Encord integrates seamlessly with cloud storage solutions like S3, which is used by a majority of our customers. This allows for easy access and filtering of data stored in personal infrastructure, enhancing workflow management and data organization.
Encord offers a range of technical integrations tailored to meet the needs of its users, including SDKs for exporting various data formats. This flexibility allows practices to implement Encord's solutions seamlessly into their existing workflows.
Encord allows seamless integration with various data systems, including cloud-based services, network drives, OneDrive, and AWS S3 shares. This flexibility ensures that users can connect their existing data sources without disruption.
Encord supports seamless data integration by allowing users to bring in cloud data and stream it into the platform. This makes it easy to create datasets and set up workflows tailored to specific project needs.